Resetting your vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) can seem like a daunting task, often associated with dealership visits and hefty bills. However, with the advancements in automotive technology, many car owners are now exploring the possibility of ECU reprogramming using an OBD2 scanner from the comfort of their garage. But is it truly feasible? And more importantly, is it safe?
This article delves into the world of Obd2 Scanner Reprogram capabilities. We’ll explore whether you can actually reprogram your ECU with an OBD2 scanner, what type of scanner you’ll need, the steps involved, potential risks, and safer alternatives if you’re hesitant to take the DIY route. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of ECU reprogramming and whether an OBD2 scanner can be your tool of choice.
Can You Really Reprogram Your ECU with an OBD2 Scanner?
The short answer is yes, reprogramming your ECU with an OBD2 scanner is indeed possible, but it’s not as straightforward as simply plugging in any scanner and pressing a button. While basic OBD2 scanners are excellent for reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes, their functionality typically stops there. These entry-level devices lack the advanced capabilities required for ECU reprogramming.
To perform ECU reprogramming, you’ll need a specialized OBD2 scanner equipped with advanced functions. These scanners go beyond basic diagnostics and offer features like ECU flashing or module programming. It’s crucial to understand that not all OBD2 scanners are created equal; choosing the right tool is paramount to successfully and safely reprogram your vehicle’s ECU. Using an inadequate scanner could lead to incomplete programming, system malfunctions, or even damage to your car’s sensitive electronics.
Essential Features of an OBD2 Scanner for ECU Reprogramming
When it comes to OBD2 scanner reprogram functionality, certain features are non-negotiable. To effectively and safely reprogram your ECU, your scanner must possess capabilities that extend far beyond basic code reading. Here’s what to look for:
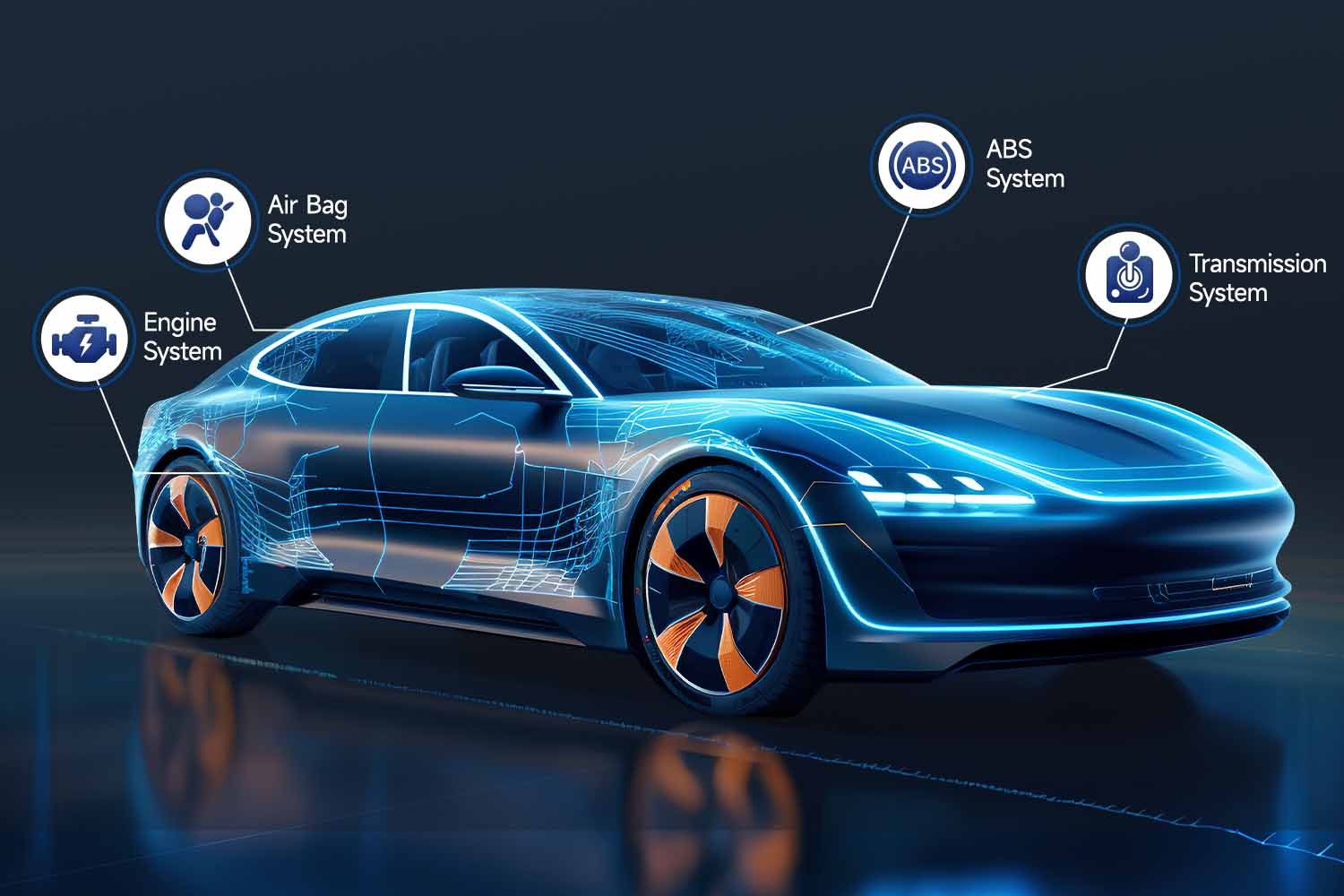
- Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities: The scanner needs to access a wide range of vehicle systems, not just the engine. This includes transmission, ABS, airbags, and other modules that interact with the ECU. Comprehensive system access ensures the scanner can communicate with and reprogram the ECU effectively.
- Bi-directional Control (Active Test): This is a critical feature. Bi-directional control allows the scanner to send commands to the vehicle’s systems, enabling you to initiate functions like ECU reprogramming. Without this, the scanner can only read data, not actively modify or reprogram modules.
- ECU Flashing/Programming Functionality: Look for explicit mentions of “ECU flashing,” “ECU programming,” or “module programming” in the scanner’s specifications. This indicates the scanner is designed to rewrite the ECU software, which is the essence of reprogramming.
- Broad Vehicle Compatibility: ECU communication protocols vary significantly between manufacturers and even models. Ensure the scanner supports a wide range of makes and models, and crucially, is compatible with your specific vehicle. Check compatibility lists carefully before purchasing.
- User-Friendly Interface: Reprogramming an ECU is a complex task. A scanner with an intuitive interface and clear instructions is essential, especially for DIY users. A well-designed interface minimizes the risk of errors during the reprogramming process.
- Regular Software Updates: Vehicle technology is constantly evolving. A scanner with updatable software ensures it remains compatible with newer vehicles and the latest ECU programming protocols. Regular updates are vital for long-term usability and effectiveness.
Step-by-Step Guide: Reprogramming Your ECU with an OBD2 Scanner
While the process can vary slightly depending on the scanner and vehicle, here’s a general step-by-step guide to OBD2 scanner reprogram, using the Foxwell NT909 as an example of an advanced tool capable of this task. Remember to always consult your scanner’s user manual and your vehicle’s repair information for specific instructions.
1. Connect the OBD2 Scanner: Locate your vehicle’s OBD2 port. It’s typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Plug your advanced OBD2 scanner, like the Foxwell NT909, securely into this port. Ensure a stable connection.
2. Turn on the Ignition (Engine OFF): Turn your car key to the “ON” position. This powers up the vehicle’s electronics and the OBD2 port, but do not start the engine. The scanner should power on automatically once connected and the ignition is on.
3. Navigate to ECU Programming Function: Using your scanner’s interface, navigate to the “ECU Programming,” “Module Programming,” or similarly named function. On the Foxwell NT909, this is usually found within the “Service” or “Advanced Functions” menu, depending on the vehicle make and model.
4. Select ECU Reprogramming/Flashing: Once in the programming menu, you may need to select the specific ECU you want to reprogram (e.g., Engine ECU, Transmission ECU). Follow the on-screen prompts carefully. The scanner will guide you through the necessary selections for your vehicle.
5. Follow On-Screen Instructions and Prompts: The scanner will display step-by-step instructions for the reprogramming process. This may involve confirming your vehicle information, downloading software updates (if necessary), and initiating the reprogramming sequence. It is crucial to follow these prompts exactly and without interruption.
6. Wait for Reprogramming to Complete: ECU reprogramming can take some time, ranging from a few minutes to over half an hour, depending on the size of the software update and the vehicle’s communication speed. Do not disconnect the scanner or turn off the ignition during this process. The scanner will display a progress bar and notify you upon completion.
7. Verify Reprogramming and Clear Codes: Once the process is complete, the scanner will typically prompt you to verify the reprogramming. Follow these final steps. It’s also advisable to perform a diagnostic scan and clear any fault codes that may have arisen during the process.
Keep in mind, tools like the Foxwell NT909 are professional-grade diagnostic systems that offer a wide array of functions beyond just ECU reprogramming. They provide real-time data, in-depth diagnostics, and bi-directional control, making them valuable assets for comprehensive vehicle maintenance and repair.
Potential Risks of DIY ECU Reprogramming
While OBD2 scanner reprogram capabilities offer convenience, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks involved in performing ECU reprogramming yourself:
- Data Loss and Driveability Issues: ECU reprogramming often involves erasing the ECU’s learned parameters, including fuel trims, idle settings, and transmission shift points. After reprogramming, your vehicle may exhibit rough idling, poor fuel economy, or sluggish performance until the ECU relearns these settings. This relearning process can take time and driving cycles.
- Masking Underlying Problems: Resetting or reprogramming the ECU can temporarily clear fault codes, masking underlying mechanical or sensor issues. While the check engine light might disappear, the root problem remains and could resurface later, potentially leading to more severe damage if left unaddressed.
- Risk of ECU Damage or “Bricking”: The most significant risk is interrupting the reprogramming process or using an incompatible or faulty scanner. This can lead to data corruption within the ECU, rendering it inoperable – often referred to as “bricking” the ECU. A bricked ECU can necessitate costly replacement or professional repair.
- Warranty Implications: Reprogramming your ECU yourself, especially with aftermarket software or tunes, can void your vehicle’s warranty, particularly powertrain warranties. Dealerships may be able to detect ECU modifications and deny warranty claims if problems arise.
Safer Alternatives to DIY ECU Reprogramming
If the risks associated with OBD2 scanner reprogram seem too significant, or if you lack confidence in performing the task yourself, several safer alternatives exist:
- Professional Mechanic Visit: A qualified mechanic has the expertise and professional-grade tools to reprogram your ECU safely and correctly. They can also diagnose underlying issues and ensure the reprogramming is appropriate for your vehicle’s needs.
- Dealership Service: Dealerships possess dealer-level diagnostic and programming tools specifically designed for your vehicle’s make and model. While typically more expensive, dealerships offer a high level of assurance that the ECU reprogramming will be performed correctly and according to manufacturer specifications.
- Specialized ECU Tuning Shops: For performance-related ECU reprogramming (tuning or remapping), specialized tuning shops employ experienced technicians and sophisticated equipment to optimize your ECU for increased power, fuel efficiency, or other specific goals.
- Battery Disconnection (For ECU Reset, Not Reprogramming): Disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for 15-30 minutes can force a basic ECU reset by cutting off power and clearing volatile memory. This is a less precise method and doesn’t reprogram the ECU, but it can sometimes resolve minor software glitches or reset learned parameters.
Conclusion: Informed Decisions about OBD2 Scanner Reprogramming
OBD2 scanner reprogram capability is a powerful feature that puts ECU control within reach of car owners and enthusiasts. However, it’s not a task to be taken lightly. While advanced OBD2 scanners offer the tools for ECU reprogramming, understanding the process, risks, and necessary precautions is paramount.
If you are comfortable with automotive technology, possess a suitable advanced OBD2 scanner, and are willing to proceed cautiously, DIY ECU reprogramming can be a viable option. However, if you are uncertain, prioritize safety and consider seeking professional assistance. Making an informed decision based on your skills, risk tolerance, and the specific needs of your vehicle is the best approach to ECU management.
FAQs
Can you program ECU with OBD2?
Yes, with advanced OBD2 scanners that support ECU programming functions. Basic scanners are not capable of ECU programming.
Can I program my ECU myself?
Yes, you can program your ECU yourself if you have the right tools, knowledge, and understand the risks involved. However, professional expertise is recommended to avoid potential issues.
Can a cheap OBD2 scanner damage an ECU?
While less likely with basic code reading functions, using a cheap or poorly designed scanner for advanced functions like ECU programming increases the risk of communication errors or sending incorrect signals that could potentially damage the ECU. Always use reputable and well-reviewed scanners for ECU reprogramming.