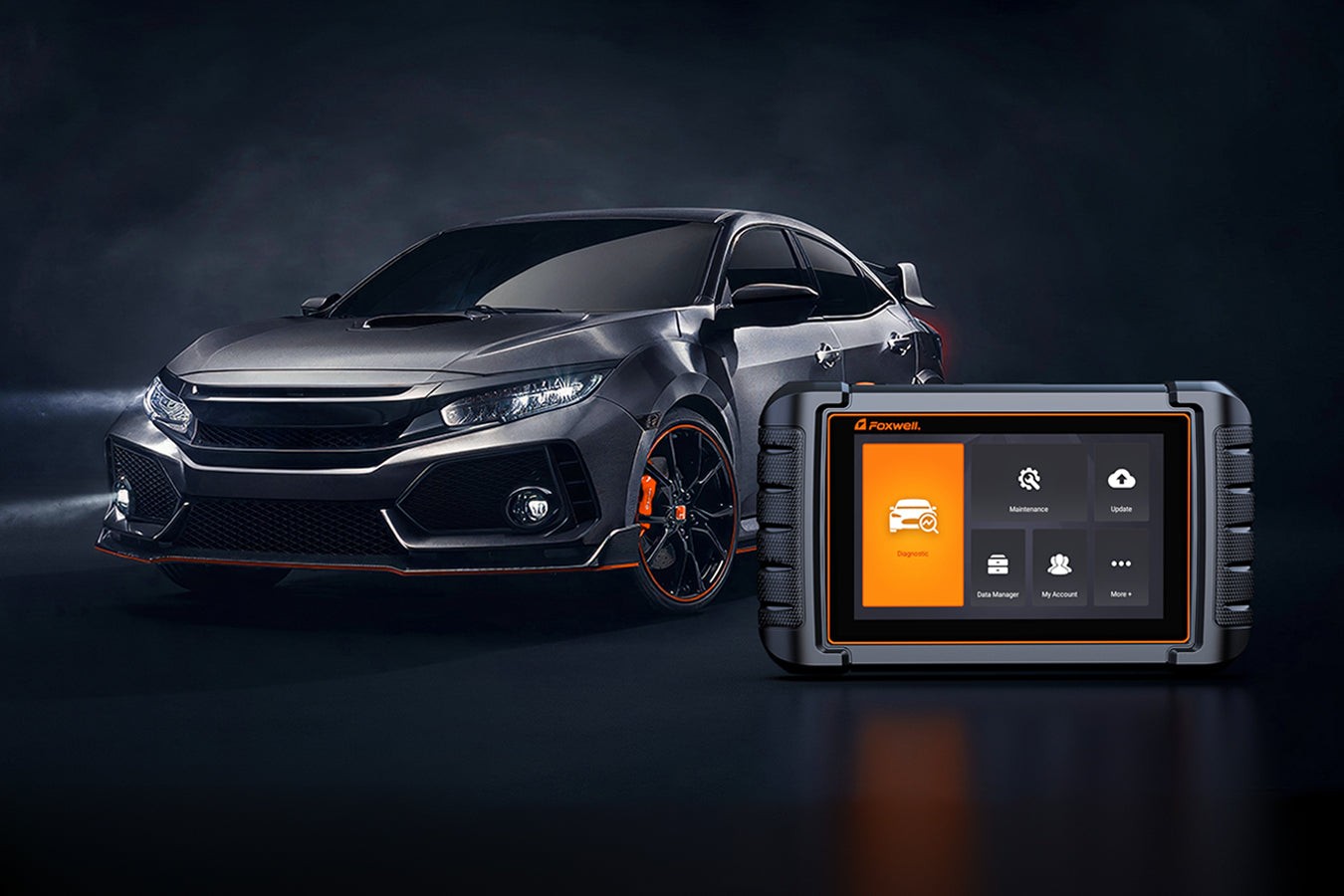
On-board diagnostics (OBD2) technology has revolutionized vehicle maintenance, becoming an essential tool for both car owners and professional mechanics. Originating from California’s emission control regulations, OBD2 systems are now a global standard, empowering vehicles to self-diagnose issues and report them efficiently. This self-diagnostic capability significantly speeds up automotive repairs and enhances vehicle safety.
For anyone looking to understand their vehicle’s health, especially the intricate workings of the transmission system, OBD2 scanners that read transmission codes are indispensable. These devices provide access to critical data regarding engine performance, emission levels, and crucially, transmission health. This insight is invaluable for proactive maintenance and accurate diagnostics.
Reading transmission codes is specifically vital for pinpointing problems within modern vehicle transmissions. Today’s transmissions are complex systems managed by numerous electronic controls and sensors. When something goes wrong, it can lead to significant issues, potentially rendering your car undrivable. An Obd2 Scanner Read Transmission Codes to help you quickly identify problems like gear slippage, solenoid malfunctions, or sensor failures. Early detection allows for timely repairs, preventing further damage and more costly fixes down the line.
How OBD2 Scanners Work for Transmission Diagnostics
OBD2 scanners operate by establishing a connection with your vehicle’s computer system through the OBD2 port, typically located beneath the dashboard. Once connected, the scanner communicates with the car’s computer to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and a range of other relevant data. This data is then processed by the scanner’s software, or a paired application, and presented to the user in an understandable format, highlighting potential issues or system performance metrics.
For transmission diagnostics, a capable OBD2 scanner read transmission codes by specifically requesting data from the transmission control module (TCM). The TCM is responsible for monitoring and controlling various aspects of the transmission, such as gear shifts, fluid pressure, and temperature. When the TCM detects a fault, it stores a specific DTC related to the transmission issue. The OBD2 scanner retrieves these codes, allowing mechanics and car owners to understand the nature of the problem within the transmission system.
Exploring Types of OBD2 Scanners for Reading Transmission Codes
The market offers a variety of OBD2 scanners, each with different capabilities and features. When it comes to reading transmission codes, not all scanners are created equal. Understanding the different types will help you choose the best tool for your needs.
Basic OBD2 Scanners: These entry-level devices are designed for fundamental diagnostics. They generally offer code reading and clearing for engine-related issues, which can be helpful for basic troubleshooting. However, many basic scanners lack the advanced functionality needed to read transmission codes. While they might be affordable and easy to use, they may not provide the depth of diagnostic information required for transmission problems.
Advanced OBD2 Scanners: Stepping up from basic models, advanced OBD2 scanners offer a broader range of features, making them suitable for enthusiasts and DIY mechanics who need more in-depth insights. These scanners often include the ability to read transmission codes, along with enhanced features like live data streaming, expanded code definitions, and sometimes bidirectional control. Live data streaming is particularly useful for transmission diagnostics, allowing you to monitor parameters like transmission temperature, gear selection, and solenoid status in real-time. Bidirectional control can also be invaluable, enabling you to command certain transmission functions for testing purposes.
Professional OBD2 Scanners: Designed for mechanics and automotive technicians, professional OBD2 scanners provide the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. These high-end devices are essential for workshops and serious professionals because they reliably read transmission codes across a wide range of vehicle makes and models. They offer advanced functions like system testing, actuation tests, and in-depth diagnostic procedures for various vehicle systems, including transmissions. Professional scanners often come with extensive vehicle coverage, regular software updates, and robust support, making them a significant investment but a powerful tool for complex diagnostics.
Smartphone-Based OBD2 Scanners: This category represents a blend of convenience and capability. Smartphone-based OBD2 scanners consist of a small hardware adapter that plugs into the OBD2 port and communicates with a smartphone app via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. Depending on the app and adapter, these systems can range from basic code readers to surprisingly comprehensive diagnostic tools. Many of the better smartphone-based scanners are capable of obd2 scanner read transmission codes and offer user-friendly interfaces, data logging, and cloud-based features. They provide portability and flexibility, allowing you to perform diagnostics virtually anywhere using your phone.
Selecting the Right OBD2 Scanner to Read Transmission Codes
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner read transmission codes is a critical decision that impacts your ability to effectively diagnose and maintain your vehicle’s transmission. With a wide array of models available, considering several key factors will ensure you make an informed choice. Compatibility, software support, user interface, and specific features are all essential aspects to evaluate.
Vehicle Compatibility: Makes and Models
The first and foremost consideration when selecting an OBD2 scanner read transmission codes is vehicle compatibility. Not all scanners support every vehicle make and model due to variations in communication protocols used by different manufacturers. Before making a purchase, always verify the scanner’s specifications to ensure it lists your vehicle’s make and model as supported. Many manufacturers provide compatibility lists on their websites, detailing the makes and models that are fully compatible with their scanners.
Manufacturer-Specific vs. Multi-Manufacturer Support
Consider whether you need manufacturer-specific or multi-manufacturer support. Some OBD2 scanners read transmission codes are designed to work specifically with vehicles from a particular manufacturer, such as BMW or Ford. These manufacturer-specific scanners often offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities and access to proprietary codes and systems not available on generic scanners. For example, a Foxwell NT510 Elite configured for BMW will provide deeper insights into BMW transmissions than a general OBD2 scanner.
On the other hand, if you own vehicles from different manufacturers or are a professional mechanic working on a variety of cars, a multi-manufacturer OBD2 scanner is a more versatile choice. Scanners like the Foxwell NT301 are designed to be broadly compatible across a wide range of makes and models, making them ideal for users who need to diagnose different vehicles regularly.
Software and Update Support for Transmission Diagnostics
Software is the heart of any OBD2 scanner read transmission codes, and regular updates are crucial to keep the scanner effective and current. Vehicle technology and diagnostic codes evolve constantly, especially in complex systems like transmissions. Software updates ensure your scanner remains compatible with the latest vehicle models and diagnostic protocols. Check if the scanner manufacturer offers regular updates, and understand how these updates are delivered (e.g., via USB, Wi-Fi, or smartphone app). Foxwell, for example, is known for providing regular software updates for models like the NT510 Elite, ensuring ongoing compatibility and feature enhancements.
User Interface and Display for Easy Transmission Code Reading
For efficient and accurate diagnostics, especially when dealing with intricate systems like transmissions, the user interface and display of an OBD2 scanner read transmission codes are paramount. An intuitive and clear interface simplifies navigation and data interpretation, making the diagnostic process smoother and less prone to errors.
Display Quality: Look for scanners with high-resolution displays that are easy to read under various lighting conditions. Backlit color displays are particularly advantageous, providing clarity in both bright sunlight and dimly lit garages. Scanners like the Foxwell NT201 feature clear, backlit displays that enhance readability in diverse environments.
User Interface Design: An intuitive user interface is just as important as display quality. Menus should be logically organized, navigation should be straightforward, and code definitions should be readily accessible. Scanners like the Foxwell NT510 Elite are praised for their user-friendly design, featuring clear menu options and comprehensive code definitions that streamline the diagnostic process.
Transmission Code Reading Capabilities: Enhancing DTC Support
Not all OBD2 scanners read transmission codes. Many basic scanners are limited to engine and emissions-related codes. Therefore, it’s crucial to verify that a scanner specifically advertises its ability to read transmission codes before you purchase it. Transmission codes often fall under manufacturer-specific or enhanced diagnostic trouble codes, requiring a more sophisticated scanner to access.
Enhanced DTC Support: Scanners that offer enhanced DTC support, such as the Foxwell NT630 Plus, are designed to read transmission codes and other system-specific codes beyond the basic OBD2 parameters. These scanners provide deeper insights into transmission issues by accessing manufacturer-specific codes and performing system tests that are not available with generic scanners.
Code Definitions: Simply reading a code is only the first step; understanding what the code means is equally important. The best OBD2 scanner read transmission codes and provide clear, understandable definitions directly on the device. Some scanners only display the raw code number, leaving you to look up the definition elsewhere. Scanners like the Foxwell NT301 include extensive built-in code definitions, simplifying the process of diagnosing transmission issues by providing immediate context and potential causes for each code.
Additional Features and Functionality for Transmission Diagnostics
Beyond the essential ability to obd2 scanner read transmission codes, additional features and functionalities can significantly enhance the value and effectiveness of an OBD2 scanner, especially for transmission diagnostics.
Live Data Streaming: Real-time data streaming is an invaluable feature for diagnosing intermittent transmission problems or monitoring system behavior under different operating conditions. A scanner that supports live data streaming allows you to view real-time parameters from the transmission system, such as fluid temperature, input and output shaft speeds, solenoid status, and gear position. This dynamic data helps in identifying issues that might not be evident from static code readings alone. The Foxwell NT301, for example, offers live data streaming for transmission parameters, enabling users to observe system performance as it happens.
Freeze Frame Data: Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of vehicle parameters at the moment a fault code is triggered. This feature provides valuable context for understanding the conditions under which a transmission problem occurred. Scanners like the Foxwell NT201 include freeze frame capability, allowing you to analyze parameters such as engine speed, vehicle speed, and transmission temperature at the time a transmission code was set. This information can be crucial in diagnosing the root cause of the issue.
System Resets and Adaptations: For certain transmission repairs and maintenance tasks, system reset and adaptation functions are essential. After replacing transmission components like solenoids or sensors, or after performing a transmission fluid change on some newer vehicles, reset and adaptation procedures may be required to ensure proper transmission operation. The Foxwell NT510 Elite offers various reset and adaptation functions specific to transmissions, such as clutch adaptation, gear learning, and transmission control module resets. These functions improve diagnostic and repair capabilities, ensuring the transmission operates correctly after maintenance or repairs.
Diagnostics for the transmission system are critical for overall vehicle maintenance. Transmission issues can severely impact vehicle performance and longevity. OBD2 scanners designed to read transmission codes provide direct access to the vehicle’s transmission health data. By connecting to the vehicle’s computer, these scanners retrieve codes related to the transmission system, enabling effective diagnosis and troubleshooting.
Step-by-Step: Connecting and Using an OBD2 Scanner to Read Transmission Codes
Connecting an OBD2 scanner read transmission codes to your vehicle is a straightforward process. Typically, the OBD2 port is located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
1. Locate the OBD2 Port: Turn off your vehicle’s ignition and locate the OBD2 port. It’s usually within easy reach under the dashboard.
2. Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner firmly into the port. Ensure it’s securely connected for proper communication.
3. Turn Ignition to ‘ON’: Turn your vehicle’s ignition to the ‘ON’ position, but do not start the engine. This provides power to the vehicle’s systems and allows the scanner to communicate with the computer.
4. Power On the Scanner: Turn on your OBD2 scanner. It should power up and begin establishing communication with the vehicle.
5. Navigate to Diagnostic Menu: Use the scanner’s menu to navigate to the diagnostic functions. Look for options like “Read Codes,” “Diagnostic Codes,” or similar.
6. Select Transmission Codes (if necessary): Some advanced scanners may allow you to select specific systems to scan. If prompted, choose “Transmission” or “Transmission Control Module (TCM)” to specifically obd2 scanner read transmission codes.
7. Read and Record Codes: The scanner will retrieve and display any stored transmission codes. Record these codes, as they are crucial for diagnosis.
8. Review Code Definitions: Use the scanner’s built-in code definitions to understand what each code means. This will provide insights into potential transmission problems.
9. (Optional) Live Data and Further Tests: Depending on your scanner, you might use live data features to monitor transmission parameters or perform additional tests as needed.
10. Disconnect Scanner: Once you have gathered the necessary information, turn off the scanner and disconnect it from the OBD2 port. Turn off the vehicle ignition.
Foxwell Diagnostics’ Foxwell NT510 Elite is a prime example of a user-friendly OBD2 scanner read transmission codes. Compatible with numerous vehicle makes, it offers comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including reading and clearing transmission codes. To begin, simply connect it to the OBD2 port and follow the on-screen prompts.
Ensuring Proper Connection for Accurate Readings
A proper connection between the OBD2 scanner read transmission codes and the vehicle is essential for accurate diagnostics. If the scanner fails to connect or you suspect an issue, check the following:
- Inspect the OBD2 Port: Ensure the OBD2 port is free from damage or debris. Bent pins or obstructions can prevent a good connection.
- Secure Connection: Make sure the scanner is firmly plugged into the port. A loose connection can lead to intermittent communication issues. Try unplugging and replugging the scanner to ensure a secure fit.
- Ignition Position: Verify that your vehicle’s ignition is in the “ON” position. Some vehicles require the ignition to be on for the scanner to communicate with the computer system.
- Scanner Power: Check that the scanner is powered on and functioning correctly. Some scanners are powered by the vehicle’s battery through the OBD2 port, while others may have their own power source.
Understanding and Interpreting Transmission Codes
Interpreting transmission codes is crucial for effective diagnosis. Most OBD2 scanners read transmission codes and provide built-in code definitions to help users understand the meaning of each code.
Utilizing Code Definitions: The Foxwell NT510 Elite and similar scanners provide detailed code definitions and potential causes for transmission-related issues. For example, a code like P0700 typically indicates a general transmission control system malfunction, while P0730 suggests an incorrect gear ratio. Understanding these definitions is key to accurately diagnosing transmission problems.
Online Resources and Repair Manuals: For further clarification or more in-depth information, you can utilize online resources and vehicle repair manuals. Foxwell Diagnostics, for instance, offers an extensive online code library with detailed explanations for various diagnostic trouble codes related to transmission systems. Vehicle-specific repair manuals can also provide valuable context and troubleshooting steps for particular codes.
Common Transmission Issues Detected by OBD2 Scanners
OBD2 scanners read transmission codes to help identify a range of common transmission problems:
-
Gear Slippage: Gear slippage occurs when the transmission unexpectedly shifts gears or fails to stay in the selected gear. This can trigger codes like P0731 (Gear 1 Incorrect Ratio) or P0732 (Gear 2 Incorrect Ratio). An OBD2 scanner read transmission codes like these and can help pinpoint issues such as worn clutch components or low transmission fluid.
-
Solenoid Malfunctions: Transmission solenoids control the flow of transmission fluid, which is essential for gear shifting. Malfunctioning solenoids can cause shifting problems and trigger codes like P0750 (Shift Solenoid A Malfunction) or P0755 (Shift Solenoid B Malfunction). Scanners like the Foxwell NT510 Elite can identify solenoid-related issues, facilitating targeted repairs.
-
Transmission Sensor Failures: Sensors monitor various aspects of transmission performance, including speed and temperature. Failures in these sensors can lead to codes such as P0715 (Input Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction) or P0720 (Output Shaft Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction). An OBD2 scanner read transmission codes related to sensor failures, enabling efficient diagnosis and repair.
Clearing Transmission Codes and Resetting the System
After diagnosing and repairing transmission problems, it’s important to clear the stored codes from the vehicle’s computer using an OBD2 scanner read transmission codes. Clearing codes ensures that the malfunction indicator lamp (check engine light) turns off and that the system is ready to detect new issues.
Using Foxwell NT510 Elite for Code Clearing: The Foxwell NT510 Elite and similar scanners make code clearing straightforward. Navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option in the scanner’s menu. Follow the prompts to clear the transmission codes and reset the system. This step is crucial to verify that the repairs have been effective and to monitor for any recurrence of the problem.
Caution Against Premature Code Clearing: Avoid clearing codes prematurely before diagnosing and addressing the underlying issue. Clearing codes without fixing the problem will only temporarily turn off the warning light, and the problem will likely return. Always diagnose and repair the issue first, and then use the OBD2 scanner read transmission codes to clear the codes after the repair is complete.
Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
Even with high-quality devices, you might encounter issues while using an OBD2 scanner read transmission codes. Troubleshooting common problems can help ensure you get the most out of your scanner.
Connectivity Issues
Connectivity problems are often related to the OBD2 port or the scanner’s connection.
- Inspect OBD2 Port: Check the vehicle’s OBD2 port for any damage or obstructions that might prevent a good connection.
- Secure the Connection: Ensure the scanner is firmly plugged into the OBD2 port. Try unplugging and replugging it to make sure it’s secure.
- Check Vehicle Power: Verify that your vehicle’s ignition is in the “ON” position and that the vehicle’s battery is not critically low. Some scanners require sufficient vehicle power to operate correctly.
Software and Firmware Issues
Software glitches or outdated firmware can sometimes cause scanner malfunctions.
- Update Software: Regularly check for software updates for your OBD2 scanner read transmission codes. Manufacturers like Foxwell release updates to fix bugs, improve functionality, and add support for new vehicles.
- Restart the Scanner: A simple restart can often resolve minor software glitches. Power off the scanner, wait a few seconds, and then power it back on.
- Factory Reset: If restarting doesn’t help, consult your scanner’s manual for instructions on performing a factory reset. This will restore the scanner to its default settings and may resolve persistent software issues.
Inconsistent or Incorrect Codes
If your OBD2 scanner read transmission codes that seem inconsistent or inaccurate, consider these steps:
- Verify with Another Scanner: If possible, use a different OBD2 scanner to verify the codes. This can help determine if the issue is with the scanner or the vehicle.
- Check Software Compatibility: Ensure that your scanner’s software is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Incompatibility can sometimes lead to incorrect code readings.
- Clear and Re-Scan: Clear the codes and re-scan the vehicle. Sometimes, temporary or spurious codes can be set. Re-scanning can provide a clearer picture of the current issues.
Display or Interface Problems
If you experience issues with the scanner’s display or user interface:
- Adjust Display Settings: Check if your scanner has settings for adjusting brightness or contrast. Adjust these settings to improve visibility.
- Clean the Display: Ensure the scanner’s display screen is clean and free from smudges or debris that could obstruct visibility.
- Restart the Scanner: For display or interface glitches, restarting the scanner can often resolve the problem.
As discussed, OBD2 scanners read transmission codes are indispensable tools for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance or repair. They provide vital insights into the health and performance of a vehicle’s transmission system, enabling early detection and resolution of potential issues. From basic DIY tasks to professional diagnostics, having the ability to obd2 scanner read transmission codes is a significant advantage.
Conclusion
When selecting an OBD2 scanner read transmission codes, prioritize compatibility with your vehicle, robust software support, a user-friendly interface, and the specific transmission code capabilities you need. Additional features like live data streaming and system reset functions further enhance the scanner’s value.
Reputable brands like Foxwell Diagnostics offer reliable scanners with comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, improving vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting efficiency. OBD2 scanners read transmission codes, connect directly to the vehicle’s computer, and identify common transmission issues, allowing for proactive maintenance and timely repairs.
Proper care and maintenance of your OBD2 scanner read transmission codes, including regular software updates, careful storage, and prompt troubleshooting of any issues, will ensure its longevity and accuracy. These devices are essential tools for vehicle diagnostics, particularly for transmission-related problems. By understanding how to select, use, and maintain these scanners, both drivers and mechanics can keep vehicles running smoothly and proactively address potential transmission issues. With a reliable OBD2 scanner read transmission codes like the Foxwell NT510 Elite, vehicle owners can confidently manage transmission diagnostics and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with a well-maintained vehicle.
FAQs
Can all OBD2 scanners read transmission codes?
No, not all OBD2 scanners are capable of reading transmission codes. This feature is typically found in more advanced or professional-grade scanners. Basic scanners often only cover engine and emissions-related codes. Always check the scanner’s specifications to confirm its ability to obd2 scanner read transmission codes before purchasing.
How often should I use an OBD2 scanner for transmission diagnostics?
It’s advisable to use an OBD2 scanner read transmission codes at least annually as part of routine vehicle maintenance. Additionally, you should use a scanner whenever you notice symptoms of transmission problems, such as unusual shifting, slipping gears, or warning lights related to the transmission. Regular checks can help catch minor issues before they escalate into major repairs.
Can an OBD2 scanner repair transmission issues?
No, an OBD2 scanner read transmission codes and diagnose potential problems, but it cannot repair them. The scanner is a diagnostic tool that helps identify the source of the issue. Once a problem is identified, you will need to perform the necessary repairs, which may involve mechanical work, replacing parts, or other maintenance procedures. The scanner helps you understand what needs fixing, but the repair work must be done separately.