Understanding your vehicle’s health is crucial, whether you manage a fleet of vehicles or own a single car. Modern vehicles are equipped with sophisticated onboard diagnostic systems, and OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) codes are a key output of these systems. Among the various types of OBD-II codes, powertrain codes are particularly important as they signal issues within the systems that power your vehicle. This guide will delve into Obd2 Powertrain Codes, explaining what they are, why they matter, and how to effectively understand and address them.
What are OBD2 Powertrain Codes?
OBD-II powertrain codes are diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) generated by your vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU) or powertrain control module (PCM). These codes are designed to alert you to potential problems within the powertrain, which encompasses the engine, transmission, and related drivetrain components. Essentially, powertrain codes are your car’s way of saying, “Hey, there’s something not quite right with how I’m making power and moving!”
These codes are standardized across most vehicles manufactured from 1996 onwards, making them a universal language for automotive diagnostics. When a sensor detects a reading outside of normal parameters within the powertrain system, the ECU registers a fault and illuminates the “Check Engine” light or “Service Engine Soon” light on your dashboard. Simultaneously, it stores a corresponding powertrain code.
To access these codes, you’ll need an OBD-II scanner or code reader. This device plugs into your vehicle’s OBD-II port, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Once connected, the scanner can retrieve stored codes, providing valuable insight into the nature of the problem.
 What OBD2 codes mean
What OBD2 codes mean
Why are Powertrain Codes Important?
Powertrain codes are critical for several reasons:
- Early Problem Detection: They provide early warnings of potential issues, allowing for timely intervention and preventing minor problems from escalating into major, costly repairs.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: Powertrain codes help pinpoint the source of a problem, guiding mechanics or DIYers to the specific system or component that requires attention. This reduces guesswork and speeds up the diagnostic process.
- Performance and Efficiency: Powertrain issues can significantly impact vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Addressing powertrain codes promptly ensures your vehicle operates optimally, saving fuel and reducing environmental impact.
- Safety: Some powertrain problems can affect vehicle safety. For example, transmission issues or engine malfunctions can lead to unpredictable vehicle behavior. Powertrain codes related to critical safety systems, like traction control or stability control, are crucial to address immediately.
- Fleet Management: For fleet managers, understanding powertrain codes is essential for maintaining vehicle uptime, scheduling preventative maintenance, and controlling repair costs across the fleet.
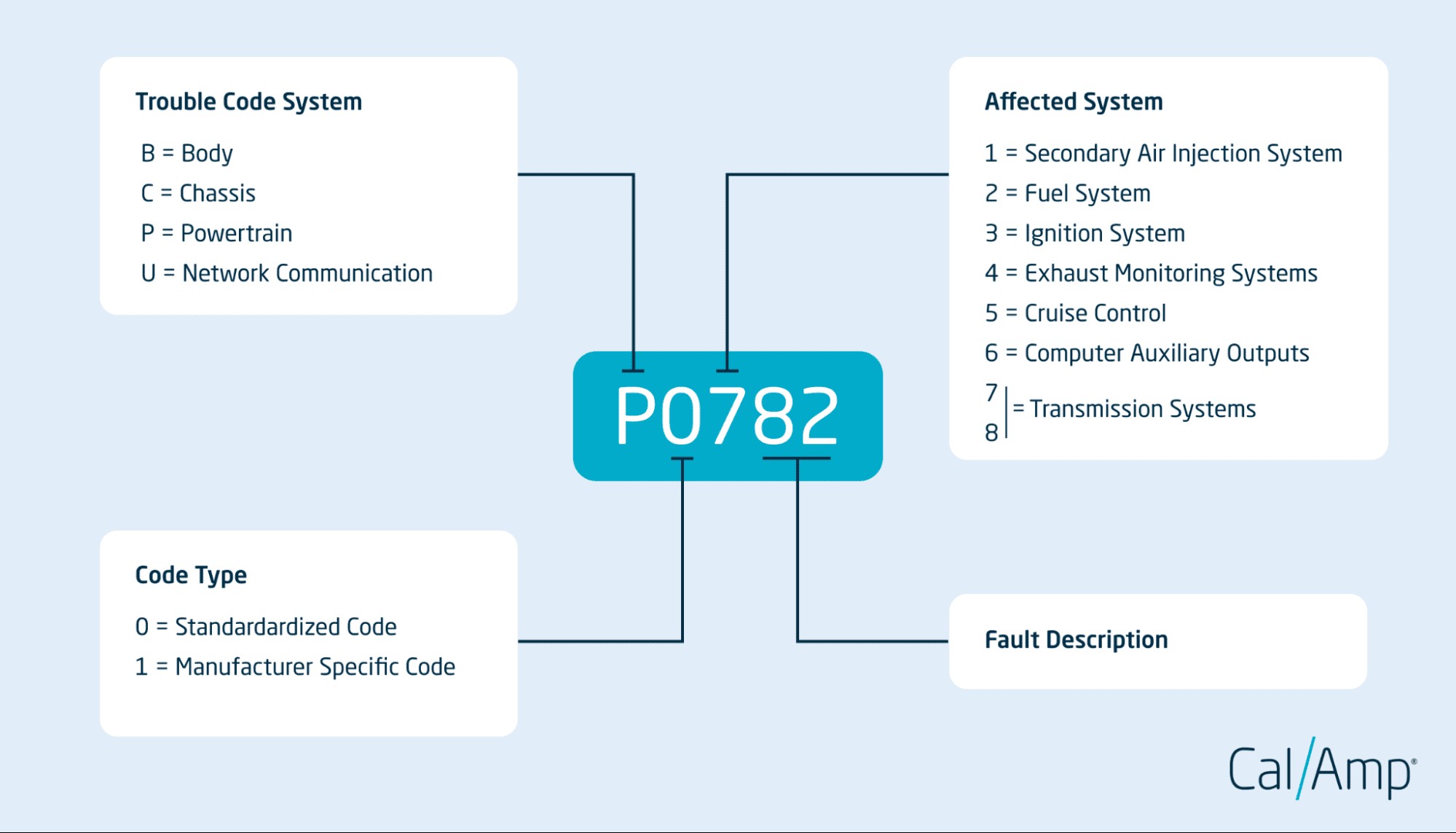
Decoding Powertrain Codes: Understanding the Structure
OBD-II codes, including powertrain codes, follow a standardized five-character format. Let’s break down each character to understand how to interpret them:
-
First Character: Trouble Code System
- P: Powertrain (Engine, Transmission, Drivetrain) – This is what we’re focusing on.
- B: Body (Body electrical systems like airbags, lights, power windows)
- C: Chassis (Mechanical systems and controllers like ABS, suspension, steering)
- U: Network Communication (Communication issues between onboard computer systems)
-
Second Character: Code Type
- 0: Standardized (Generic) Code – These codes are common across all makes and models.
- 1: Manufacturer-Specific Code – These codes are defined by the vehicle manufacturer and provide more specific information.
- 2, 3: Reserved for future use (less common)
-
Third Character: Affected System
This digit indicates the specific subsystem within the powertrain that is experiencing a problem. Common categories include:- 0: Fuel and Air Metering and Auxiliary Emission Controls
- 1: Fuel and Air Metering
- 2: Fuel and Air Metering – Injector Circuit
- 3: Ignition System or Misfire
- 4: Auxiliary Emission Controls
- 5: Idle Control System and Auxiliary Inputs
- 6: Computer and Output Circuit
- 7, 8: Transmission
-
Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Code
These two digits provide a specific numerical identifier that, combined with the preceding characters, precisely defines the fault. For example, within the “Fuel and Air Metering” (digit 1 or 2), codes like P0100 to P0199 relate to issues with the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor, intake air temperature sensor, and related circuits.
Example: P0301
- P: Powertrain
- 0: Standardized Code
- 3: Ignition System or Misfire
- 01: Specific code indicating misfire in cylinder 1
This code P0301, therefore, tells you there is a powertrain-related issue, specifically a standardized misfire detected in cylinder 1 of the engine’s ignition system.
Common OBD2 Powertrain Code Categories and Examples
Powertrain codes cover a wide range of potential issues. Here are some common categories and examples to give you a better understanding:
Engine-Related Powertrain Codes
-
Misfire Codes (P0300-P0399): Indicate that one or more cylinders are not firing correctly. Examples include:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0301-P0312: Cylinder Specific Misfire (e.g., P0301 – Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected)
Misfires can be caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, or low compression.
-
Fuel and Air Metering Codes (P0100-P0299): Relate to issues with the air-fuel mixture. Examples include:
- P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0172: System Too Rich (Bank 1)
These codes can stem from problems with the MAF sensor, oxygen sensors, fuel injectors, fuel pump, or vacuum leaks.
-
Oxygen Sensor Codes (P0130-P0167, P0420-P0439): Indicate problems with the oxygen sensors that monitor exhaust gases or catalytic converter efficiency. Examples include:
- P0131: O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
Oxygen sensor issues can result from sensor failure, exhaust leaks, or catalytic converter problems.
-
Engine Temperature Codes (P0115-P0120, P0125-P0129): Indicate problems with engine coolant temperature sensor or thermostat. Examples:
- P0118: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input
- P0128: Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature)
These can be caused by a faulty temperature sensor, thermostat issues, or cooling system problems.
Transmission-Related Powertrain Codes
-
Transmission Performance Codes (P0700-P0799): Indicate general transmission problems or issues with specific functions. Examples:
- P0700: Transmission Control System Malfunction
- P0741: Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off
These can point to problems with solenoids, valve body, torque converter, or internal transmission components.
-
Gear Ratio Codes (P0715-P0740, P0750-P0770): Indicate issues with gear selection or ratios. Examples:
- P0717: Input Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal
- P0730: Incorrect Gear Ratio
These codes often relate to sensor failures, internal mechanical issues, or solenoid problems within the transmission.
Drivetrain-Related Powertrain Codes
While less common as distinct OBD-II categories, some powertrain codes can indirectly relate to drivetrain components, particularly if they impact the engine or transmission’s ability to deliver power effectively. For example, issues affecting engine torque output or transmission gear selection will ultimately affect the drivetrain.
Diagnosing and Addressing Powertrain Codes
When a powertrain code appears, follow these steps for effective diagnosis and resolution:
- Record the Code: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve and note down all present codes. Multiple codes can provide a broader picture of the problem.
- Research the Code: Consult a reliable OBD-II code database or repair manual to understand the specific meaning of each code and potential causes. Websites like OBD-Codes.com or reputable automotive forums can be helpful resources.
- Visual Inspection: Before diving into complex diagnostics, perform a visual inspection of the engine bay. Check for:
- Loose or disconnected hoses and wires
- Fluid leaks
- Damaged or corroded components
- Unusual noises or smells
- Component Testing: Based on the code and your research, you may need to test specific components. For powertrain codes, this could involve testing:
- Sensors (MAF, oxygen, temperature, speed sensors) with a multimeter
- Ignition coils with an ignition tester
- Fuel injectors for resistance and spray pattern
- Vacuum lines for leaks
- Professional Diagnosis (If Needed): If you’re not comfortable with automotive diagnostics or the problem is complex, consult a qualified mechanic. They have advanced tools and expertise to accurately diagnose and repair powertrain issues.
- Repair and Verification: Once the issue is identified and repaired, clear the OBD-II codes using a scanner. Then, test drive the vehicle to ensure the problem is resolved and the “Check Engine” light does not reappear. In some cases, a drive cycle may be required for the system to fully reset and confirm the repair.
Preventing Powertrain Codes
Preventing powertrain codes is always better than dealing with repairs. Proactive maintenance is key:
- Regular Scheduled Maintenance: Adhere to your vehicle manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule. This includes oil changes, filter replacements, spark plug replacements, fluid checks and flushes, and timing belt/chain maintenance.
- Use Quality Fluids and Parts: Use high-quality engine oil, transmission fluid, coolant, and other fluids that meet or exceed manufacturer specifications. Similarly, when replacing parts, opt for reputable brands known for quality and durability.
- Address Minor Issues Promptly: Don’t ignore warning signs like unusual noises, rough idling, or decreased performance. Address minor issues before they escalate and trigger powertrain codes.
- Proper Driving Habits: Avoid harsh acceleration, excessive idling, and neglecting your vehicle’s needs. Smooth, consistent driving and attentive vehicle care can extend the life of powertrain components.
Managing Powertrain Codes for Fleets
For fleet managers, handling powertrain codes efficiently is crucial for minimizing downtime and controlling costs. Consider these strategies:
- Centralized OBD-II Monitoring: Implement a telematics system that provides real-time OBD-II code data for all fleet vehicles. This allows for proactive monitoring and early detection of issues.
- Prioritized Maintenance Scheduling: Use OBD-II data to prioritize maintenance and repairs based on code severity and vehicle usage. Address critical powertrain codes immediately to prevent breakdowns.
- Driver Training: Educate drivers on recognizing warning signs and reporting vehicle issues promptly. Encourage pre-trip inspections to catch potential problems early.
- Data Analysis for Preventative Maintenance: Analyze historical OBD-II data to identify trends and patterns in powertrain issues across the fleet. This can inform preventative maintenance schedules and help predict potential failures.
Conclusion
OBD2 powertrain codes are invaluable tools for understanding your vehicle’s inner workings and maintaining its health. By learning to decode and interpret these messages, you can proactively address potential issues, ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity for your vehicle or fleet. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a vehicle owner wanting to be more informed, understanding powertrain codes empowers you to take better care of your vehicles and keep them running smoothly for miles to come.