In the evolving landscape of automotive technology, vehicle diagnostics and reprogramming have become increasingly sophisticated. At techcarusa.com, we are dedicated to demystifying these advancements, making them accessible to both seasoned professionals and automotive enthusiasts. This guide focuses on OBD2 pass-through devices, essential tools that are revolutionizing how we interact with modern vehicles. We aim to provide an in-depth understanding of these devices, their functionalities, and their pivotal role in today’s automotive repair and maintenance.
This article will explore what OBD2 pass-through devices are, how they function within the framework of the SAE J2534 standard, and why they are indispensable for modern automotive work. We will delve into their practical applications, discuss the challenges associated with their use, and highlight how these tools are empowering automotive professionals and hobbyists alike. Join us as we navigate the intricacies of OBD2 pass-through technology, ensuring you are well-informed and ready to leverage its potential.
Understanding OBD2 Pass-Through Devices and the J2534 Standard
An OBD2 pass-through device is a hardware interface that acts as a communication bridge between a computer and a vehicle’s Electronic Control Units (ECUs) via the standardized OBD-II port. These devices are engineered to comply with the SAE J2534 standard, a critical protocol established by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). This standard is the backbone that allows a single diagnostic tool to communicate effectively with a multitude of vehicle brands and models, eliminating the previously cumbersome need for brand-specific equipment.
The J2534 standard essentially provides a universal “language” for automotive diagnostics and ECU reprogramming. It ensures that certified OBD2 pass-through devices can seamlessly interact with vehicle systems, regardless of the manufacturer. This standardization is paramount for independent repair shops and technicians, offering them the capability to perform advanced diagnostics and reprogramming across a diverse range of vehicles, thereby fostering fair competition and enhancing service accessibility for vehicle owners.
Key advantages of utilizing OBD2 pass-through devices rooted in the J2534 standard include:
- Universal Application: A single OBD2 pass-through device can service numerous vehicle brands, negating the necessity for multiple, expensive OEM-specific tools.
- Economic Efficiency: Reducing the need for proprietary tools translates to significant cost savings for repair facilities and technicians.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Precision: OBD2 pass-through devices provide deep access to a vehicle’s ECUs, facilitating more accurate and comprehensive diagnostics, leading to superior repair outcomes.
- Support for Right to Repair Initiatives: By democratizing access to diagnostic and reprogramming tools, OBD2 pass-through devices support consumer rights and promote a more competitive automotive service industry.
Think of an OBD2 pass-through device as a translator, enabling your diagnostic software to speak directly with your vehicle’s complex electronic systems. It converts generic commands from the software into the specific protocols understood by the vehicle’s ECUs, and vice versa, ensuring seamless communication for diagnostics and reprogramming tasks.
J2534-1 vs. J2534-2: Key Differences
To fully grasp the capabilities of OBD2 pass-through devices, it’s important to understand the evolution of the J2534 standard through its two primary versions:
- J2534-1: This initial iteration of the standard laid the groundwork for basic diagnostic functions and ECU reprogramming. It established the fundamental protocols for communication and was a significant step towards standardization.
- J2534-2: Building upon J2534-1, this enhanced version incorporates additional protocols and improved reprogramming functionalities. J2534-2 offers broader coverage and more sophisticated diagnostic and reprogramming options, accommodating the increasing complexity of modern vehicle systems.
Understanding these versions helps in appreciating the progressive development of OBD2 pass-through technology and its expanding role in automotive servicing. Newer devices often support both standards, ensuring compatibility with a wider range of vehicles and diagnostic operations.
Alt text: OBD2 pass-through device facilitating data exchange between diagnostic software and vehicle ECUs for comprehensive vehicle analysis.
How OBD2 Pass-Through Devices Function in Vehicle Diagnostics
To appreciate the effectiveness of OBD2 pass-through devices, it’s crucial to understand their operational mechanisms. This involves examining both the hardware and software components and the step-by-step process they facilitate for vehicle diagnostics and ECU reprogramming.
Components of an OBD2 Pass-Through System:
- OBD2 Pass-Through Hardware: This physical device connects to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and serves as the interface between the vehicle’s ECUs and the diagnostic tool. It is designed to reliably transmit data and commands.
- J2534 Compliant Software: This software, installed on a computer or diagnostic tool, is engineered to communicate with vehicles using the J2534 standard via the pass-through device. It initiates communication, interprets vehicle data, and executes reprogramming instructions.
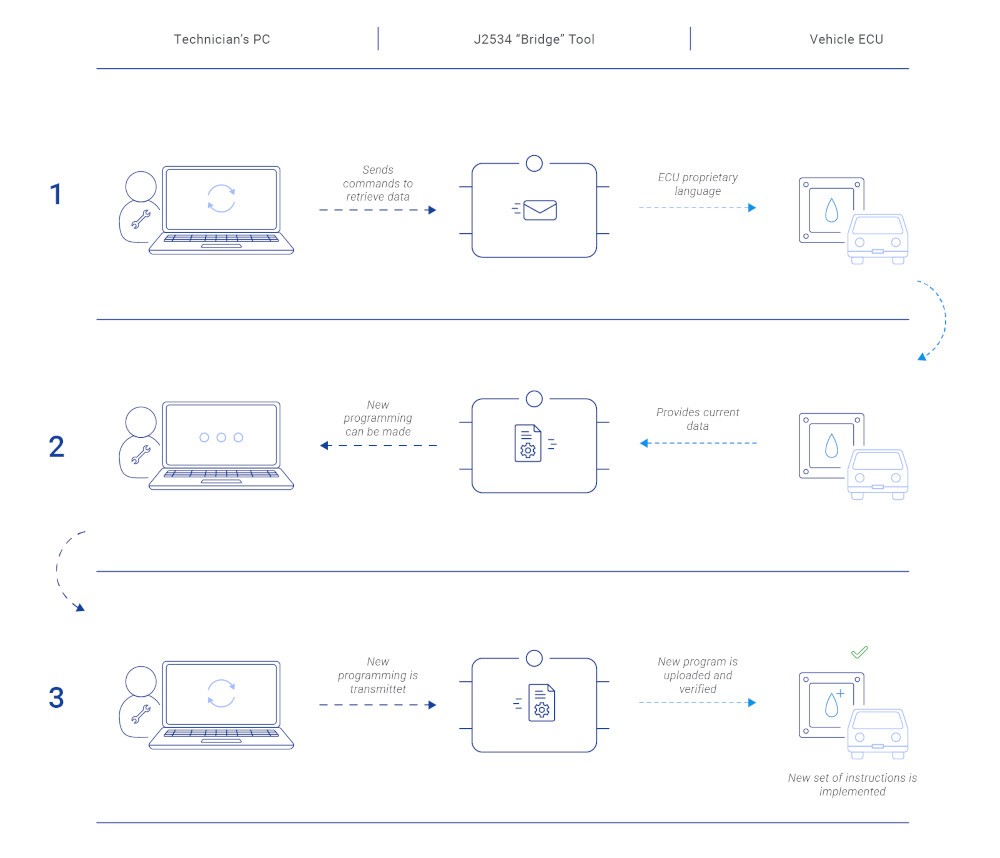
Step-by-Step Communication with an OBD2 Pass-Through Device
Let’s break down the process of how an OBD2 pass-through device enables communication between diagnostic software and a vehicle’s ECUs, from initial connection to advanced ECU reprogramming:
-
Physical Connection via OBD-II Port:
- The OBD-II port, typically located beneath the dashboard, is the access point for connecting the OBD2 pass-through device. This port is the standardized gateway for accessing the vehicle’s electronic network.
- Connecting is straightforward: simply plug the OBD2 pass-through device into the vehicle’s OBD-II port to establish a secure hardware link.
-
Initiating Communication:
- Once connected, the J2534 software on the diagnostic computer begins establishing communication with the vehicle’s ECUs through the pass-through device. This involves sending initial signals to identify and connect with the various ECUs present in the vehicle.
- The software automatically recognizes the vehicle’s systems, preparing them for data exchange and diagnostic procedures.
-
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Retrieval:
- The diagnostic software, via the OBD2 pass-through device, can now request and receive DTCs stored in the vehicle’s ECUs. These codes are crucial for identifying malfunctions within the vehicle’s systems. The software deciphers these codes, providing technicians with clear diagnostic information.
- Reading DTCs allows for precise problem identification and a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s health.
-
ECU Reprogramming and Software Updates:
- Beyond diagnostics, OBD2 pass-through devices facilitate ECU reprogramming. The J2534 software can update ECU firmware by sending new software or calibration files, enhancing vehicle performance or rectifying software-related issues.
- By following software prompts, technicians can upload updated ECU firmware, ensuring the vehicle operates with the latest software versions for optimal performance and efficiency.
This step-by-step process showcases how OBD2 pass-through devices streamline communication, enabling comprehensive diagnostics and effective ECU reprogramming, making complex vehicle servicing tasks more manageable and efficient.
| Diagnostic Software Command | OBD2 Pass-Through Device Action | Vehicle ECU Response | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Request diagnostic trouble codes” | Translates command to ECU-specific protocol | ECU retrieves and prepares DTCs | – |
| – | Sends translated command to ECU | ECU processes request | – |
| – | Receives ECU response in proprietary language | ECU sends DTCs | – |
| – | Converts ECU response to standard diagnostic software language | – | – |
| Diagnostic software displays translated DTCs | – | – | User gains access to vehicle’s diagnostic information |
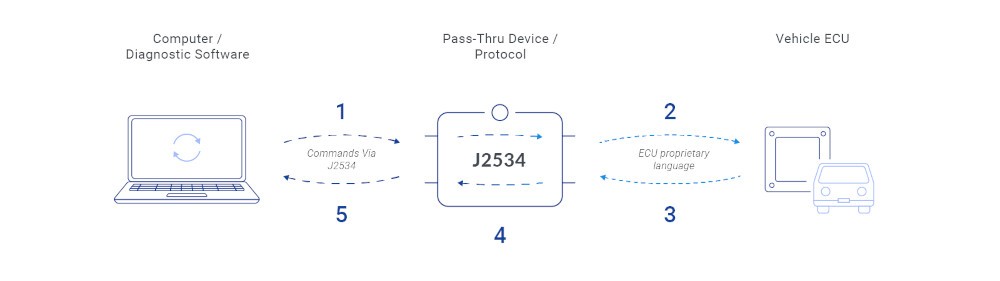


Alt text: Visual representation of OBD2 pass-through device as a J2534 standard interface for reprogramming vehicle electronic control units.
Practical Applications and Benefits of OBD2 Pass-Through Devices
OBD2 pass-through devices are not just theoretical tools; they are highly practical and versatile instruments used across a broad spectrum of automotive service scenarios. Let’s explore some key applications and real-world examples that underscore their value in vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
Diagnostic Applications
- Reading and Interpreting DTCs: When a vehicle’s malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), commonly known as the check engine light, illuminates, OBD2 pass-through devices are crucial for reading the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in the ECUs. These codes are vital for pinpointing the source of vehicle problems.
- Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes: After addressing the issues indicated by DTCs, OBD2 pass-through devices can be used to clear these codes, effectively turning off the check engine light and resetting the vehicle’s diagnostic system.
ECU Reprogramming and Software Management
- ECU Software Updates: OBD2 pass-through tools enable technicians to update the software within a vehicle’s ECUs. These updates, often provided by vehicle manufacturers, are essential for improving vehicle performance, resolving software bugs, or implementing recall-related fixes.
- Vehicle Customization and Performance Tuning: Beyond standard updates, advanced users and specialized tuning shops utilize ECU reprogramming via OBD2 pass-through devices to customize vehicle settings for enhanced performance or specific operational requirements.
Real-Time Data Monitoring and Analysis
- Live Data Streaming for Diagnostics: OBD2 pass-through devices can monitor and stream live data from numerous sensors throughout the vehicle. This real-time data is invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues or problems that do not consistently trigger DTCs.
- Performance Monitoring and Optimization: Automotive technicians and performance enthusiasts use live data monitoring to fine-tune vehicle performance parameters and ensure all systems are functioning at their peak efficiency.
Real-World Examples of OBD2 Pass-Through Device Utilization
- Independent Automotive Repair Facilities: Independent repair shops benefit significantly from OBD2 pass-through devices by being able to service a wide array of vehicle makes and models with a single, standardized tool. This eliminates the prohibitive cost of investing in multiple OEM-specific diagnostic tools. They can efficiently perform tasks from reading and clearing DTCs to complex ECU reprogramming.
- Automotive Dealership Service Centers: Dealerships utilize OBD2 pass-through devices for routine software updates, executing manufacturer recall campaigns, and advanced diagnostics. For instance, a dealership might use an OBD2 pass-through device to reprogram an ECU to rectify an emissions control issue identified in a recent vehicle recall.
- Fleet Vehicle Maintenance Operations: Companies managing large fleets of vehicles employ OBD2 pass-through tools to ensure consistent vehicle maintenance and performance across their entire fleet. Regular diagnostics and software updates help minimize downtime, reduce maintenance expenses, and maintain optimal vehicle operational efficiency.
Advantages of Integrating OBD2 Pass-Through Devices
- Increased Operational Efficiency: OBD2 pass-through devices streamline the diagnostic and reprogramming processes, significantly reducing the time required to identify and resolve vehicle issues.
- Cost-Effectiveness for Businesses: By consolidating the toolset needed for servicing multiple vehicle brands, OBD2 pass-through devices offer substantial cost savings in equipment investment and maintenance.
- Improved Vehicle Reliability and Performance: Regular software updates and thorough diagnostics facilitated by OBD2 pass-through devices contribute to enhanced vehicle performance, extended vehicle lifespan, and improved overall reliability.
- Enhanced Customer Service in Repair Sectors: For automotive service providers, the ability to efficiently service a diverse range of vehicles translates to improved customer satisfaction through quicker turnaround times and comprehensive service offerings.
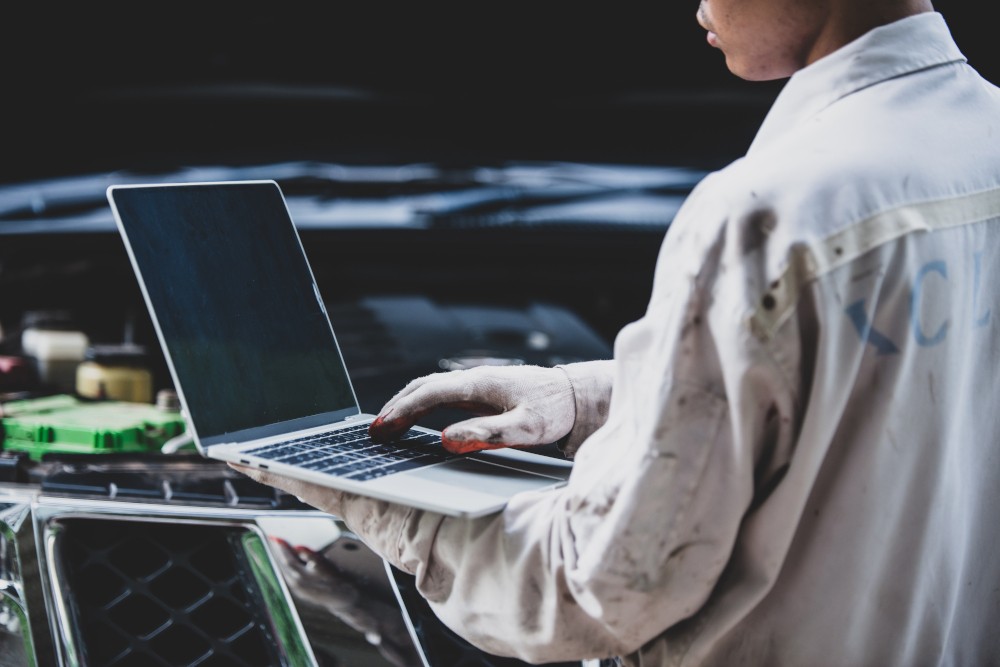
Alt text: Experienced car mechanic utilizing an OBD2 pass-through device in a vehicle to conduct thorough diagnostic checks.
By integrating OBD2 pass-through devices into their workflows, technicians and automotive service centers can deliver more comprehensive, efficient, and cost-effective services, ultimately benefiting vehicle owners through improved vehicle performance and reliability.
Navigating Challenges and Considerations with OBD2 Pass-Through Devices
While OBD2 pass-through devices offer numerous advantages, it’s important to acknowledge and understand the challenges and considerations associated with their use. Awareness of these potential issues and knowing how to mitigate them is crucial for successful diagnostics and reprogramming.
Common Challenges in OBD2 Pass-Through Device Application
-
Vehicle Compatibility Limitations:
- Issue: Not all vehicles are fully compliant with the J2534 standard. Older vehicles or certain manufacturers might employ proprietary systems that do not readily interface with J2534-compliant OBD2 pass-through devices.
- Solution: Always verify vehicle compatibility before using an OBD2 pass-through device. Consult compatibility lists provided by device manufacturers or utilize vehicle information databases to confirm J2534 support for the specific vehicle model and ECU systems.
-
Complexity of Operation:
- Issue: Effectively using OBD2 pass-through devices requires a degree of technical expertise. Understanding vehicle ECU systems, diagnostic trouble codes, reprogramming procedures, and the operation of diagnostic software is essential.
- Solution: Invest in comprehensive training and education. Many OBD2 pass-through device manufacturers offer training programs, detailed tutorials, and user manuals. Start with basic diagnostic tasks and progressively advance to more complex procedures to build proficiency and confidence.
-
Software and Firmware Management:
- Issue: Maintaining up-to-date software and firmware for OBD2 pass-through devices is critical for ensuring compatibility, optimal performance, and access to the latest vehicle protocols. Outdated software can lead to communication failures and unsuccessful reprogramming attempts.
- Solution: Regularly check for and install software and firmware updates from the device manufacturer. Enable automatic update features if available and subscribe to manufacturer notifications to stay informed about new releases and essential updates.
Addressing Limitations and Potential Risks
-
Limited Vehicle Coverage:
- Limitation: Despite the broad compatibility of J2534, some vehicles, particularly older models or those from niche manufacturers, may not be fully supported.
- Mitigation: For vehicles with limited J2534 support, having access to OEM-specific diagnostic tools may be necessary. Maintain a resource of alternative tools or consider specialized services for such vehicles.
-
Reprogramming Errors and Risks:
- Limitation: ECU reprogramming carries inherent risks. Interruptions during the process, such as power loss or software glitches, can potentially damage the ECU, leading to vehicle malfunction.
- Mitigation: Ensure a stable power supply to the vehicle throughout the reprogramming process. Use a reliable battery maintainer and ensure a stable internet connection if software updates are downloaded online. Follow manufacturer-recommended procedures meticulously and use high-quality, certified OBD2 pass-through equipment.
-
Initial Learning Curve:
- Limitation: For technicians unfamiliar with J2534 standards and OBD2 pass-through technology, there can be a steep initial learning curve.
- Mitigation: Embrace continuous learning and hands-on practice. Participate in industry forums, attend workshops and training sessions, and seek mentorship from experienced professionals to accelerate skill development and overcome initial challenges.
Practical Tips for Effective OBD2 Pass-Through Device Use
- Always Verify Compatibility: Prioritize checking vehicle and ECU compatibility with J2534 before initiating any diagnostic or reprogramming tasks.
- Invest in Quality Equipment and Training: Opt for reputable, high-quality OBD2 pass-through devices and invest in thorough training for your technicians to maximize tool effectiveness and minimize risks.
- Maintain Up-to-Date Software: Regularly update your OBD2 pass-through device software and firmware to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with the latest vehicle models and protocols.
- Ensure Stable Operating Conditions: During ECU reprogramming, ensure the vehicle has a stable power supply and avoid conducting updates over unreliable internet connections to prevent data corruption and system failures.
- Adhere to Manufacturer Guidelines: Strictly follow the guidelines and procedures provided by OBD2 pass-through device and software manufacturers to minimize errors and ensure successful outcomes.
- Seek Support When Necessary: Don’t hesitate to seek assistance from experienced technicians, online communities, or manufacturer technical support when encountering challenges or complex diagnostic scenarios.
By proactively addressing these challenges and adhering to best practices, automotive professionals can effectively leverage OBD2 pass-through devices to their full potential, ensuring accurate diagnostics, successful reprogramming, and enhanced service quality.
Alt text: AutoPi TMU CM4 device showcasing its platform adaptability for OBD2 pass-through and advanced vehicle diagnostics.
Conclusion: Embracing OBD2 Pass-Through Technology for Advanced Vehicle Diagnostics
OBD2 pass-through devices, underpinned by the SAE J2534 standard, are transformative tools in modern automotive diagnostics and repair. They offer a standardized, cost-effective, and highly capable approach to interacting with the complex electronic systems of today’s vehicles. By understanding their functionalities, applications, and potential challenges, automotive professionals and enthusiasts can harness the power of OBD2 pass-through technology to achieve superior diagnostic accuracy, efficient ECU reprogramming, and enhanced vehicle performance.
As automotive technology continues to advance, the importance of OBD2 pass-through devices will only grow. Embracing these tools is not just about keeping up with industry standards; it’s about equipping yourself with the means to deliver exceptional service, ensure vehicle reliability, and drive innovation in automotive care.
If you are ready to elevate your vehicle diagnostic capabilities or have any inquiries about integrating OBD2 pass-through solutions into your operations, do not hesitate to contact us at techcarusa.com. Our team is dedicated to supporting your journey into advanced vehicle diagnostics and helping you maximize the benefits of OBD2 pass-through technology. Reach out today to explore how these devices can revolutionize your approach to automotive maintenance and repair.
