Experiencing an engine overheat can be a vehicle owner’s nightmare, triggering concerns about potential damage and costly repairs. The sudden illumination of warning lights on your dashboard is never a welcome sight. For drivers of Ford vehicles, including popular models like the F-150, Escape, and Fusion, the appearance of the Obd2 Code P1299 can be particularly alarming. This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) signals a critical issue related to engine temperature.
If your vehicle has flagged the P1299 error code, this comprehensive guide will provide you with a deeper understanding of the problem. We’ll explore the underlying causes, associated symptoms, and effective repair strategies, along with estimated costs. Equipped with this knowledge, you can approach the issue with confidence and take informed steps to resolve it.
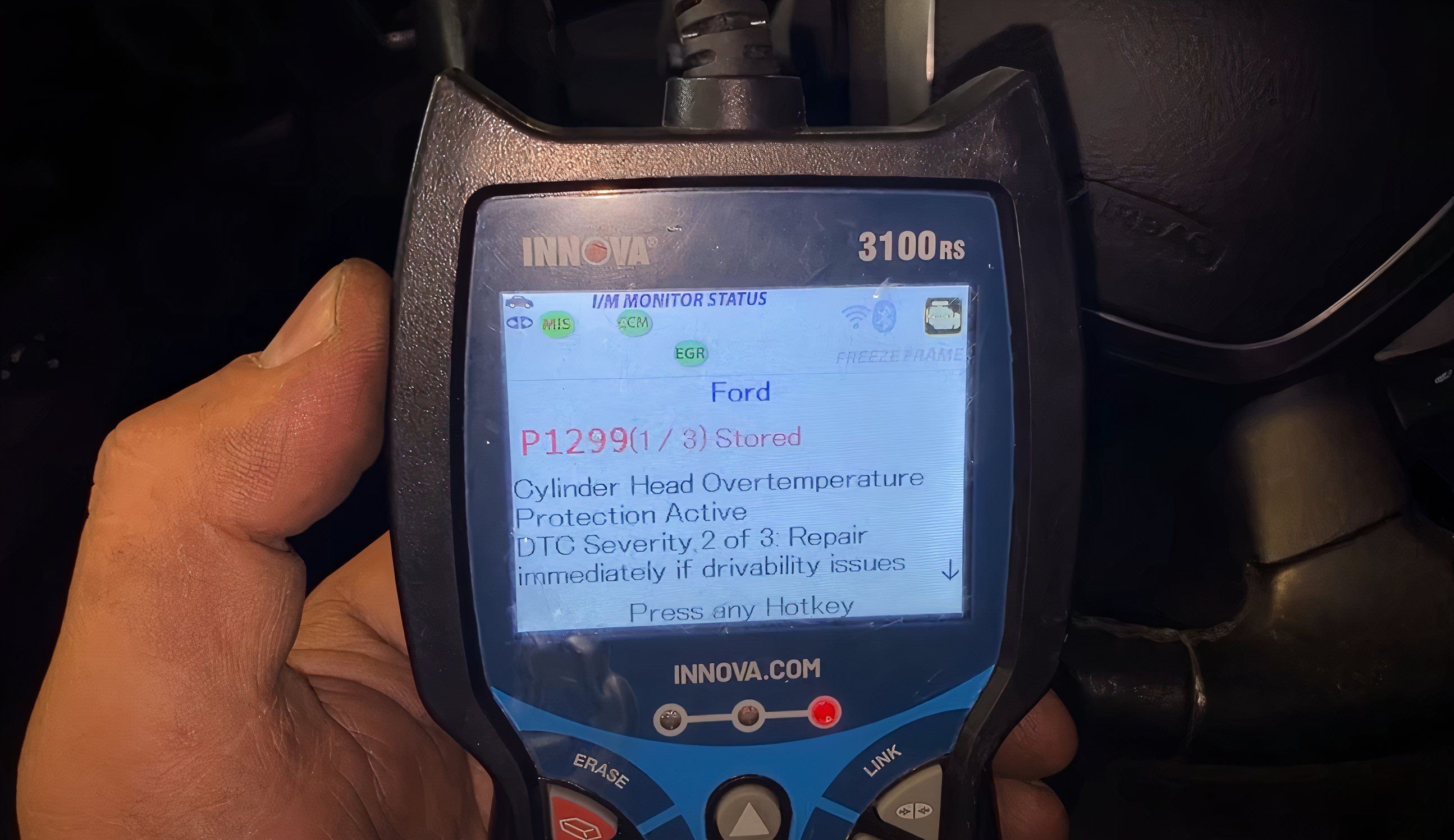
Understanding OBD2 Code P1299: Cylinder Head Overtemperature Protection Active
The P1299 fault code, specifically “Cylinder Head Overtemperature Protection Active,” is triggered in vehicles equipped with a Cylinder Head Temperature (CHT) sensor. This sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the temperature of the engine’s cylinder head(s). Modern engines, particularly those with aluminum cylinder heads, are susceptible to damage from overheating, including warping.
When the engine temperature exceeds safe operating parameters, the vehicle’s computer, known as the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or Vehicle Control Module (VCM), detects this critical condition via the CHT sensor. In response, the PCM initiates a fail-safe cooling strategy. This strategy is designed to prevent severe engine damage by actively reducing engine temperature.
The fail-safe mode often involves the PCM alternately disabling fuel injectors. This clever tactic turns engine cylinders into air pumps, which helps to dissipate heat and lower the overall engine temperature. If the overheating persists and reaches a dangerously high level, the PCM may take more drastic action, shutting off all fuel injectors and ultimately disabling the engine to prevent catastrophic damage.
Common Causes of OBD2 Code P1299
The OBD2 code P1299 can stem from a variety of underlying issues within your vehicle’s cooling system or related components. Identifying the precise cause is crucial for effective repair. Here are some of the most frequent culprits:
- Low Coolant Level: Insufficient coolant is a primary cause of overheating. Coolant is essential for absorbing and dissipating engine heat. A low coolant level reduces the system’s capacity to regulate temperature effectively.
- External Coolant Leaks: Leaks in the cooling system, whether from hoses, the radiator, water pump, or gaskets, lead to coolant loss and can quickly result in overheating.
- Airbound Cooling System: Air pockets trapped within the cooling system can impede coolant circulation, creating hot spots and leading to inaccurate temperature readings and overheating.
- Restricted Radiator or Condenser: Blockages from debris, insects, or bent fins on the radiator or condenser restrict airflow, reducing their cooling efficiency.
- Worn or Loose Water Pump Accessory Belt: The water pump belt drives the water pump, which circulates coolant. A worn or loose belt may slip, reducing or stopping coolant flow.
- Faulty Cooling Fan: The cooling fan provides essential airflow, especially at low speeds or when stationary. A malfunctioning fan can lead to insufficient cooling, particularly in hot conditions.
- Faulty Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor: An inaccurate coolant temperature sensor can provide incorrect data to the PCM, potentially triggering the P1299 code even if the engine isn’t actually overheating.
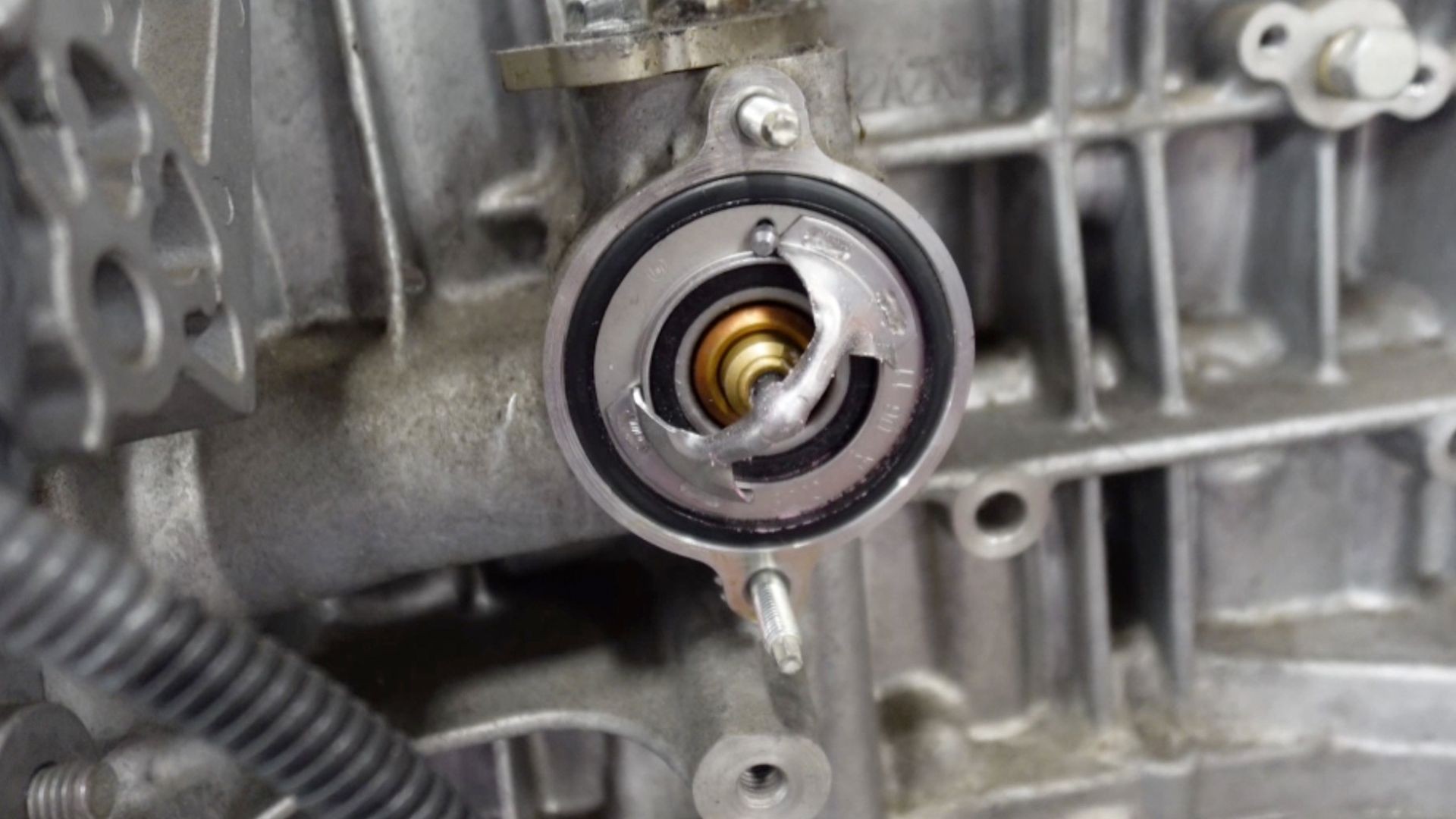
- Faulty Cylinder Head Temperature Sensor: Similarly, a failing CHT sensor may give false high-temperature readings, activating the P1299 code and fail-safe mode unnecessarily.
- Clogged Heater Core: A blocked heater core restricts coolant flow within the system, impacting overall cooling efficiency.
- Restricted Cooling System: Internal blockages within coolant passages due to corrosion, debris, or improper coolant can severely limit cooling capacity.
- Faulty Water Pump: A failing water pump may not circulate coolant effectively, leading to overheating. Impeller damage or seal failure are common water pump issues.
Symptoms Associated with OBD2 Code P1299
When the OBD2 code P1299 is active, you’ll likely notice several symptoms indicating an engine overheating condition and the PCM’s response. These symptoms can range from subtle warnings to more significant performance issues:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: This is the most common and immediate symptom. The check engine light will illuminate on your dashboard to alert you to a detected problem.
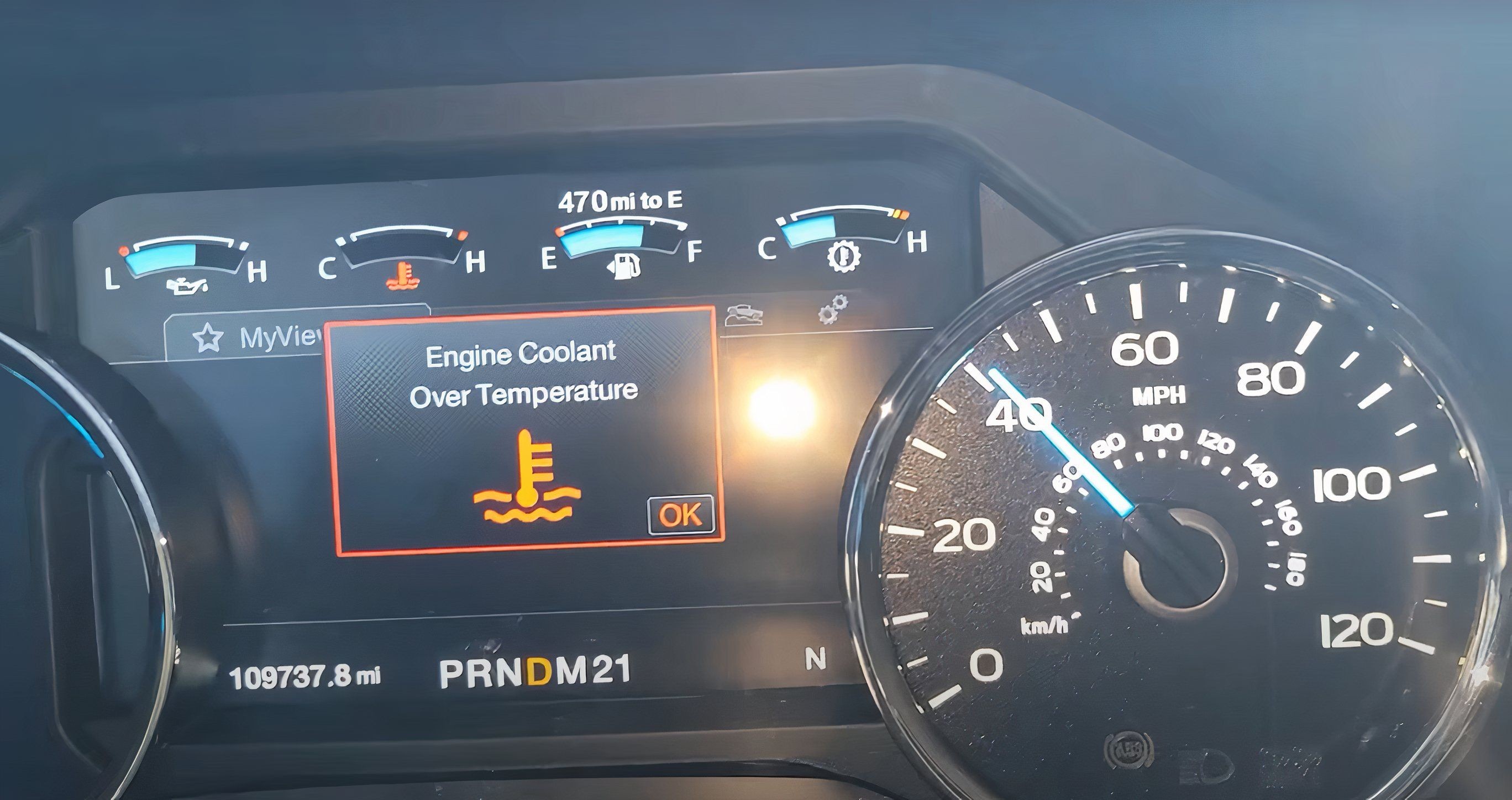
- Overheating Engine: The engine temperature gauge may read higher than normal, or you might observe steam or a burning smell emanating from the engine bay.
- Cylinder Misfires: As the PCM disables fuel injectors to cool the engine, you may experience engine misfires or rough running, particularly at idle or low speeds.
- Disabled Engine: In severe cases of overheating, the PCM may completely shut down the engine to prevent critical damage.
- Reduced Power: The fail-safe cooling strategy, by disabling injectors, inherently reduces engine power and performance.
- Reduced Fuel Economy: Engine inefficiency due to overheating and the fail-safe mode can lead to decreased fuel economy.
- Limp Mode: The vehicle may enter limp mode, a severely restricted operating mode designed to limit engine stress and allow you to reach a service location.
- Failed Emissions Testing: An overheating engine and related malfunctions can cause increased emissions, potentially leading to a failed emissions test.
Is It Safe to Drive with Code P1299?
The presence of OBD2 code P1299 is a serious warning. It directly indicates that your engine’s cylinder head temperature has exceeded safe limits. Driving with an active P1299 code is strongly discouraged and can lead to significant engine damage.
While the PCM’s fail-safe cooling mode is designed to mitigate overheating and allow you to move the vehicle to safety, it is not intended for continuous driving. The reduced power and potential for engine shutdown make it unsafe and impractical to operate the vehicle under normal driving conditions.
If you must move the vehicle, proceed with extreme caution. Closely monitor the engine temperature gauge. If the temperature gauge climbs beyond the three-quarter mark towards the maximum hot range, immediately pull over and shut off the engine to allow it to cool down. Continuing to drive under overheating conditions can result in warped cylinder heads, cracked engine blocks, blown head gaskets, and other severe and expensive engine failures. Prioritize getting your vehicle professionally diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible.
Diagnosing and Fixing OBD2 Code P1299
Addressing the OBD2 code P1299 promptly is crucial to prevent further engine damage. Here’s a step-by-step approach to diagnosing and fixing the issue:
-
Confirm the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to verify that the P1299 code is active. This ensures accurate diagnosis and avoids unnecessary repairs.
-
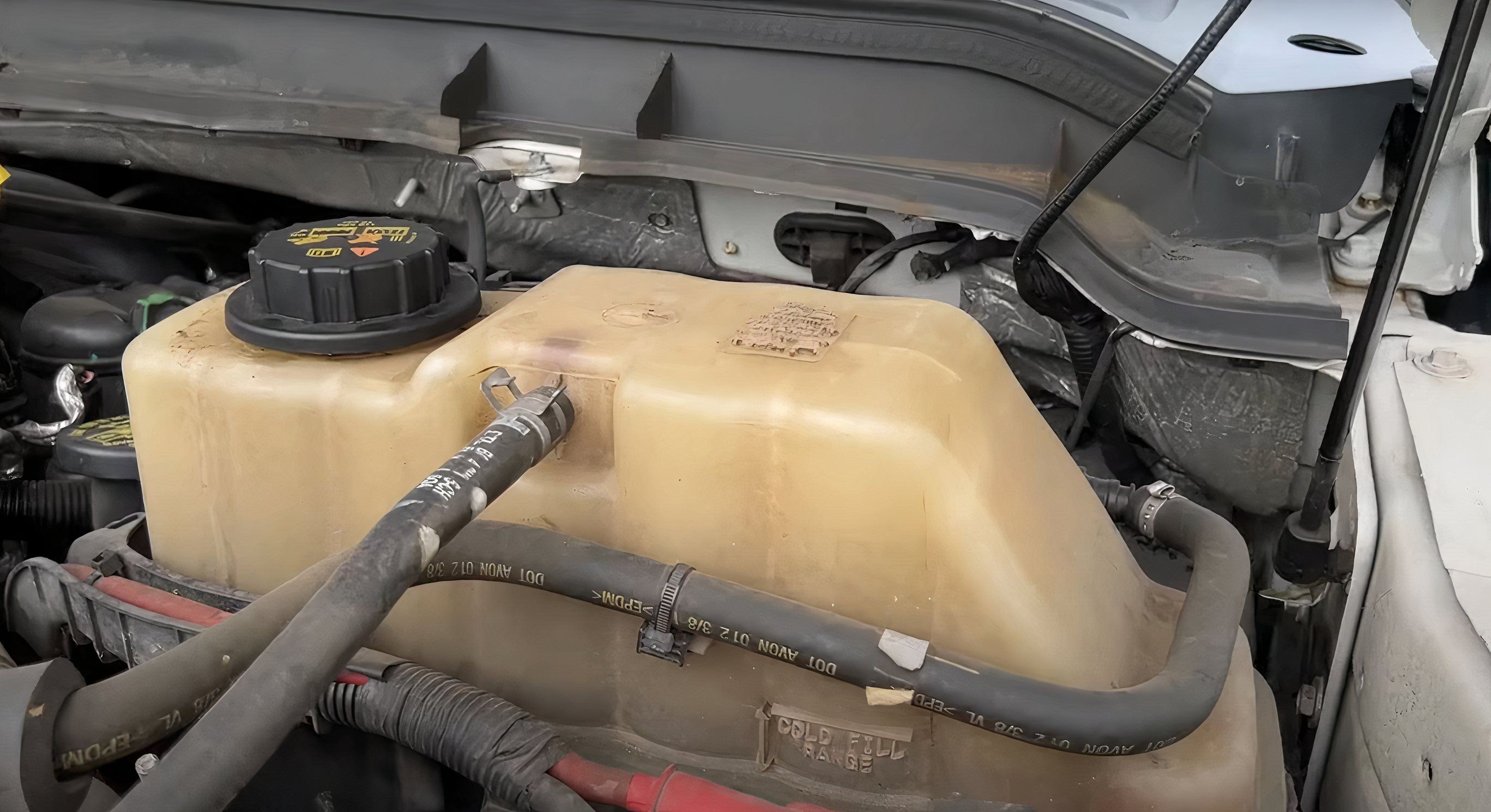
Check Coolant Level: Begin by checking the coolant level in the radiator and coolant reservoir. Ensure it is at the recommended level. Note if the coolant is excessively low, which suggests a leak. Also, verify that the correct type of coolant is used for your vehicle.
-
Inspect for Coolant Leaks: Carefully examine the engine bay for any signs of coolant leaks. Look for:
- Puddles of coolant under the vehicle.
- Visible leaks around hoses, radiator, water pump, thermostat housing, and cylinder head gaskets.
- White or crusty residue near hose connections or other cooling system components.
- Steam or coolant smell coming from the engine bay.
You may need to remove plastic under-engine shields to gain a clear view of potential leaks. Repair any identified leaks.
-
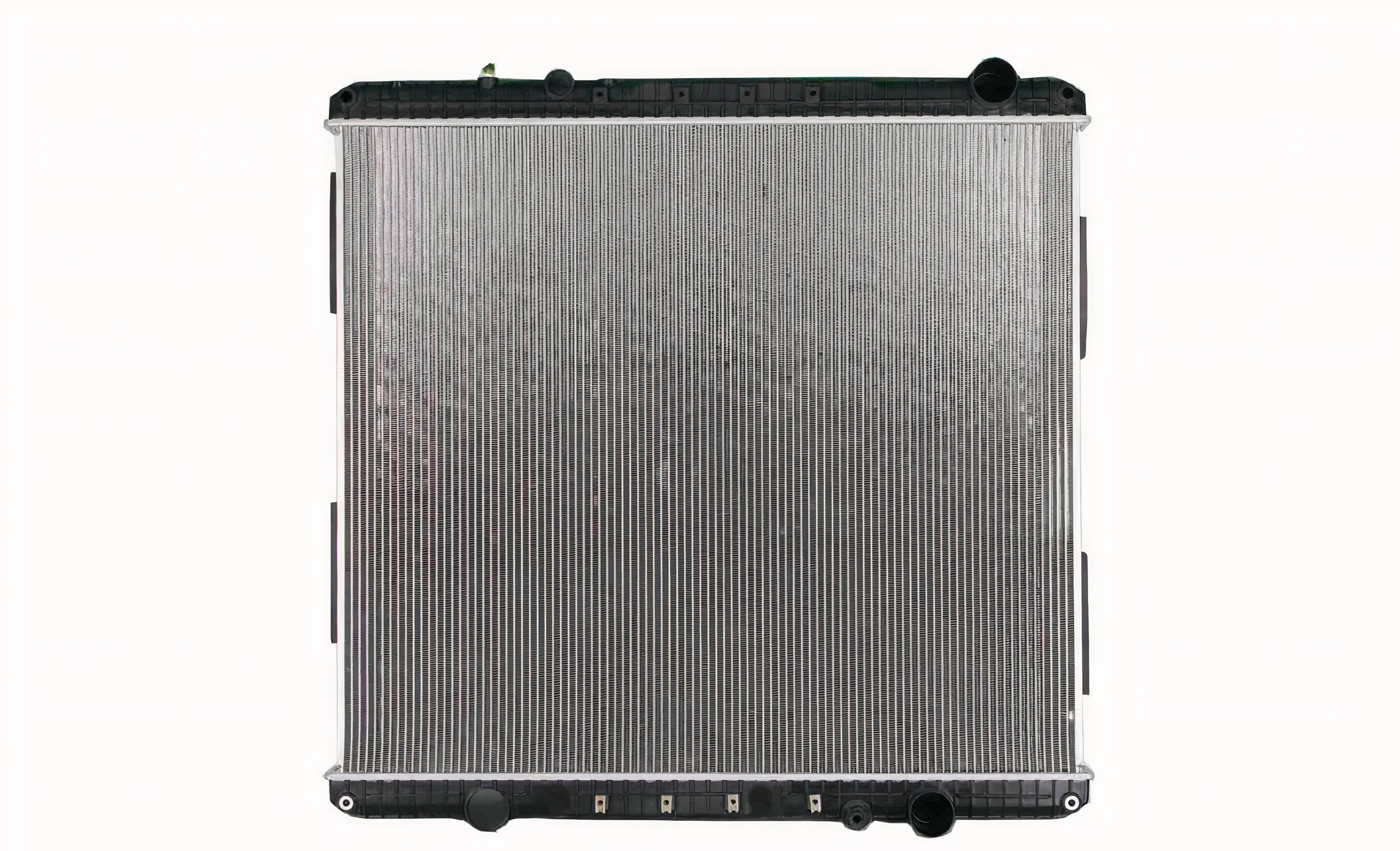
Clean Radiator and Condenser: Inspect the radiator and condenser (located in front of the radiator) for obstructions. Remove any debris such as leaves, bugs, or dirt that may be blocking airflow. Straighten any bent fins that restrict airflow. Ensure the radiator and condenser are clean and free of obstructions.
-
Bleed the Cooling System: If the coolant level was low or the system was opened for any reason, air may be trapped inside. Follow your vehicle manufacturer’s recommended procedure to bleed the cooling system and remove any air pockets.
-
Test Temperature Sensors: A faulty coolant temperature sensor or cylinder head temperature sensor can trigger the P1299 code. Use a digital multimeter to test the resistance and voltage of these sensors according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Replace any sensors that are out of specification.
-
Professional Diagnosis: If you’ve checked these common causes and the P1299 code persists, or if you are not comfortable performing these checks yourself, it’s advisable to consult a qualified automotive technician. Overheating can be caused by more complex mechanical issues like a failing water pump, thermostat, or even a blown head gasket. Professional technicians have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose and repair these more intricate problems.
Cost to Repair OBD2 Code P1299
The cost to fix the OBD2 code P1299 can vary significantly depending on the underlying cause of the overheating. Minor issues like low coolant or a faulty sensor will be considerably less expensive to repair than major mechanical failures. Here are some general cost estimates for common repairs related to P1299, based on data from RepairPal:
- Radiator Replacement (Ford Escape example): Can range up to $1,200.
- Water Pump Replacement (Ford Fusion example): Approximately $550 to $615.
- Cooling Fan Replacement (Ford F-150 example): Around $650.
- Head Gasket Replacement: A major repair, potentially costing upwards of $2,300 or more.
Component Cost Estimates (Parts Only):
| Component | Cost Estimate |
|---|---|
| Coolant hose(s) | $15 – $150 |
| Temperature sensor(s) | $10 – $75 |
| Radiator | $150 – $900 |
| Water pump | $100 – $250 |




It’s always wise to start by checking the simpler, less expensive potential causes first. Addressing P1299 early can prevent more extensive and costly engine damage. While some repairs can be tackled by experienced DIYers, complex issues are best left to professionals to ensure correct diagnosis and repair, ultimately saving you money and preventing further problems down the road.
*Sources: RepairPal