The Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) is a critical component in modern vehicles, designed to minimize harmful emissions and ensure environmental compliance. This system captures fuel vapors from the fuel tank and carburetor, preventing them from escaping into the atmosphere and contributing to air pollution. Beyond its environmental role, a properly functioning EVAP system is also essential for optimal vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
To ensure your EVAP system is working correctly, especially when you suspect issues or see a check engine light, an OBD2 scanner is an invaluable tool. Since its widespread adoption in 1996, the On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system has become the standard for vehicle diagnostics. OBD2 scanners empower both professional mechanics and car enthusiasts to access real-time data about their vehicle’s health and perform specific tests, including the crucial EVAP system test.
The role of OBD2 scanners in modern car diagnostics is multifaceted. They go beyond simply reading error codes. They help pinpoint the root causes of engine problems, monitor engine performance, and verify that your vehicle operates within emission regulations. In today’s complex vehicles, an OBD2 scanner is not just a troubleshooting tool; it’s a window into your car’s operational performance, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing minor issues from escalating into costly repairs.
In this guide, we will delve into the workings of the EVAP system, explore how to conduct an EVAP test using an OBD2 scanner, and provide insights on interpreting test results and taking appropriate action. This information is vital for anyone looking to enhance their understanding of vehicle maintenance and keep their car running smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding the Fundamentals of the EVAP System
The Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system is a cornerstone of modern automotive engineering, meticulously designed to prevent fuel vapor release into the environment. Its primary function is to capture gasoline vapors from the fuel tank and engine, store them temporarily, and then reintroduce them into the engine for combustion. This process not only significantly reduces harmful hydrocarbon emissions but also contributes to improved fuel economy.
Key Functions Within the EVAP System
The EVAP system operates through a series of key components and processes working in harmony:
Vapor Capture: Fuel vapors naturally form in the fuel tank and carburetor (in older vehicles), whether the car is running or parked. The EVAP system is engineered to capture these vapors and direct them towards the charcoal canister for storage.
Vapor Storage: The charcoal canister, filled with activated carbon, acts like a sponge, absorbing and storing fuel vapors. This prevents the vapors from venting into the atmosphere and causing pollution.
Purge Cycle: When the engine is running, engine vacuum opens a purge valve, drawing the stored fuel vapors from the charcoal canister into the engine’s intake manifold. These vapors are then burned during normal combustion, effectively recycling them instead of releasing them as pollutants.
Vent Control: A vent control valve regulates the flow of fresh air into the charcoal canister. This valve is crucial for the purging process and maintaining stable pressure within the EVAP system.
Common EVAP System Problems and Symptoms
Despite its robust design, the EVAP system is not immune to issues. Problems can arise that trigger the check engine light on your dashboard. Here are some of the most common EVAP system problems:
- Loose or Damaged Gas Cap: A simple but frequent issue is a gas cap that is not properly tightened or has a worn-out seal. This allows fuel vapors to escape, leading to system inefficiency and increased emissions.
- Vacuum Leaks in Hoses or Lines: Cracks, breaks, or loose connections in vacuum hoses or lines can disrupt the pressure balance within the system, hindering vapor flow and causing leaks.
- Faulty Purge Valve: If the purge valve sticks open or malfunctions, it can cause excessive vapor flow to the engine at inappropriate times, potentially affecting engine performance and triggering error codes.
- Saturated or Damaged Charcoal Canister: Over time, the charcoal canister can become saturated with fuel or damaged, reducing its capacity to store and release vapors effectively.
- Electrical and Sensor Issues: The EVAP system relies on various sensors and solenoids for its operation. Malfunctions in these electrical components can lead to incorrect signals being sent to the engine control unit (ECU), triggering false warnings and error codes.
Understanding these components and potential problems is the first step in diagnosing EVAP system issues, often with the aid of an OBD2 scanner. The next step is to learn how to perform an EVAP test using an OBD2 scanner, which will be discussed in detail in the following sections.
Leveraging OBD2 Scanners for Effective EVAP Testing
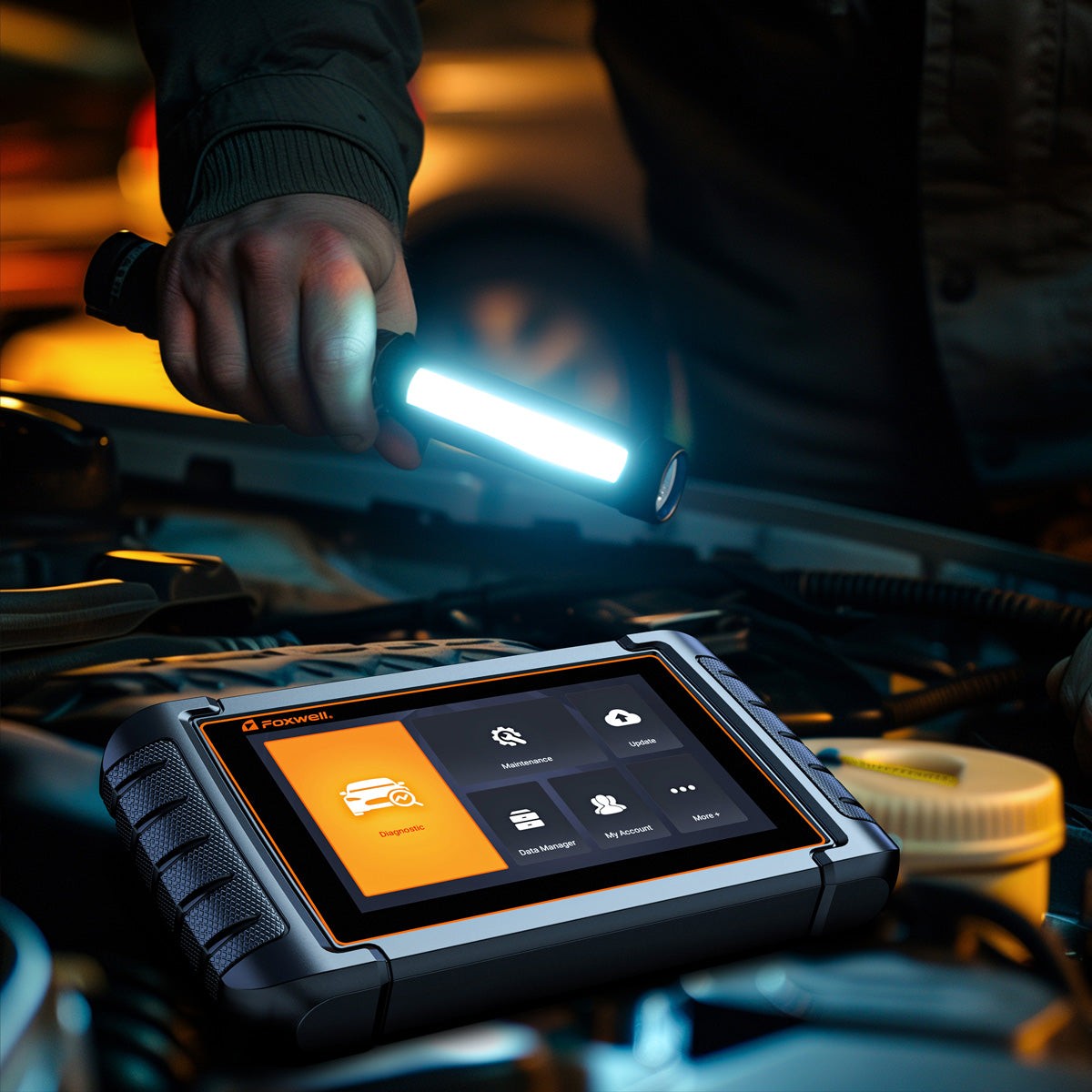
OBD2 scanners are indispensable tools for diagnosing modern vehicles, and their capabilities extend significantly into testing the Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system. These scanners are not just code readers; they offer advanced functionalities specifically designed to monitor, diagnose, and troubleshoot EVAP system malfunctions. Let’s explore the key features of OBD2 scanners that are particularly beneficial for EVAP testing, highlighting popular models like the Foxwell NT530 and NT650 Elite.
Essential OBD2 Scanner Features for EVAP Diagnostics
Bi-Directional Control: This advanced feature allows the scanner to go beyond simply reading data. Bi-directional control enables the scanner to send commands to the vehicle’s computer, allowing users to activate and test specific EVAP system components. For example, you can use bi-directional control to command the vent and purge valves to open and close, verifying their functionality and responsiveness.
Real-Time Data Monitoring: OBD2 scanners provide live data streams related to the EVAP system. This includes monitoring fuel tank pressure, vacuum levels, and sensor readings in real-time. This capability is crucial for identifying intermittent issues or pinpointing leaks and blockages within the vapor recovery system. Monitoring live data during an EVAP system test can reveal subtle anomalies that static code reading might miss.
Advanced Diagnostic Functions: High-end OBD2 scanners are equipped with enhanced diagnostic functions tailored for the EVAP system. These functions often include automated tests that simulate normal operating conditions to assess the performance of each component under various scenarios. These tests can help verify the system’s integrity and identify issues that might not be immediately apparent.
Foxwell Scanners: Leading Tools for EVAP System Analysis
Foxwell is a well-regarded brand in automotive diagnostic tools, and their NT530 and NT650 Elite models are particularly well-suited for EVAP system diagnostics:
Foxwell NT530:
- Comprehensive Manufacturer-Specific Diagnostics: The NT530 offers in-depth diagnostic coverage for a wide range of vehicle manufacturers. This means it can access detailed, manufacturer-specific fault codes and diagnostic routines, crucial for accurately diagnosing complex EVAP system issues that may vary between car brands.
- Actuation Tests: The NT530 supports actuation tests, allowing users to directly control EVAP system components via the scanner. This function is invaluable for isolating faulty components by manually activating them and observing their response.
Foxwell NT650 Elite:
- Special Service Functions: The NT650 Elite expands on the NT530’s capabilities with a range of special service functions, including EVAP system tests, EPB reset, oil service reset, DPF regeneration, and more. This makes it a versatile tool for comprehensive vehicle maintenance and diagnostics.
- Automated EVAP System Tests: The NT650 Elite can initiate automated EVAP system self-tests. These tests run pre-programmed diagnostic routines that check for leaks and other malfunctions without requiring manual component activation, streamlining the diagnostic process.
Both the Foxwell NT530 and NT650 Elite provide robust capabilities for thorough EVAP system analysis. Their ability to interface deeply with the vehicle’s onboard computer ensures accurate data retrieval and component testing, leading to more efficient and precise diagnoses of EVAP-related problems. Equipped with such a scanner, performing an EVAP test becomes a manageable and efficient task, ensuring both environmental compliance and optimal vehicle performance.
Step-by-Step Guide: Conducting an EVAP Test with an OBD2 Scanner
Performing an EVAP test using an OBD2 scanner is a crucial procedure for maintaining your vehicle’s emissions system and overall health. This test helps identify leaks and malfunctions in components like the vent valve, purge valve, and charcoal canister. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to conduct an EVAP test using an OBD2 scanner, like the Foxwell NT530 or NT650 Elite.
Preparation: Vehicle and OBD2 Scanner
Vehicle Preparation:
- Park on Level Ground: Ensure your vehicle is parked on a level surface for accurate test results.
- Engine Off: Turn off the engine completely and ensure the ignition is off.
- Fuel Level: Verify that your fuel tank is between 1/4 and 3/4 full. Most vehicles require this fuel level for the EVAP test to initiate correctly.
- Cold Engine: Ideally, the engine should be cold. A cold start is generally required for accurate EVAP system testing. Let the vehicle sit for several hours if it has been recently driven.
- Seal Vehicle: Close all windows, doors, and ensure the fuel cap is tightly sealed. A properly sealed system is essential for accurate leak detection.
OBD2 Scanner Setup:
- Charge Scanner: Ensure your OBD2 scanner is fully charged or has sufficient battery life for the duration of the test.
- Software Update: Update your scanner’s software to the latest version. This ensures compatibility with newer vehicles and access to the most accurate diagnostic data and test routines.
Performing the EVAP Test: Connection, Initialization, and Diagnosis
Connecting the Scanner:
- Locate OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual if you are unsure of its exact location.
- Connect Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the vehicle’s OBD2 port firmly.
- Power On: Turn on the OBD2 scanner. Turn the vehicle’s ignition to the “ON” position (without starting the engine) as instructed by your scanner.
Initializing the Test:
- Vehicle Selection: Using your Foxwell NT530 or NT650 Elite, navigate to the vehicle selection menu and input your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Navigate to EVAP Test: From the main menu, select “Diagnosis,” then “Control Modules.” Locate and select the “Powertrain Control Module” (PCM) or “Engine Control Module” (ECM). Within this menu, find and select “EVAP System Test” or a similar option, which might be located under “Service Functions” or “Special Functions” depending on your scanner model.
- Start EVAP Test: Follow the on-screen prompts to initiate the EVAP system test. The scanner may ask for confirmation that the fuel level is within the required range and that the vehicle has been off for a sufficient period.
Executing the EVAP Test:
- System Activation: The OBD2 scanner will command the vehicle’s computer to perform the EVAP test. This typically involves sealing the system, activating the vent and purge valves, and monitoring the system pressure.
- Monitor Test Progress: Observe the scanner’s display for real-time data and test progress. The Foxwell scanners provide live readings and status updates during the test. Pay close attention to pressure readings. A pressure drop indicates a potential leak in the system.
Analyzing Test Results:
- Check Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Once the test is complete, the scanner will display any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) detected. Common EVAP system DTCs include P0442 (small leak), P0455 (large leak), and P0441 (incorrect purge flow).
- DTC Lookup and Interpretation: Use the scanner’s built-in DTC lookup function to understand the meaning of each code. Foxwell scanners have comprehensive DTC databases with code definitions and troubleshooting tips.
- Further Diagnostics: Based on the test results and DTCs, you may need to perform further diagnostics. This could involve visually inspecting specific components like the gas cap, purge valve, charcoal canister, and vacuum hoses for damage or leaks. A smoke test, performed by a professional, can be very effective in locating small leaks.
Post-Diagnosis Actions:
- Repair and Replace: Based on your diagnosis, repair or replace any faulty components. A common fix is replacing a worn gas cap or damaged vacuum hose.
- Clear DTCs: After completing repairs, use your Foxwell scanner to clear all EVAP system DTCs from the vehicle’s ECU. This resets the system and turns off the check engine light.
- Re-Test: It’s advisable to repeat the EVAP test after repairs to ensure no new codes are present and that the issue has been successfully resolved.
By following these steps with a capable OBD2 scanner like a Foxwell NT530 or NT650 Elite, you can effectively diagnose and address EVAP system issues, ensuring your vehicle remains environmentally compliant and performs optimally.
Maintaining Your Vehicle’s EVAP System for Longevity
Regular maintenance is key to preventing common EVAP system problems and extending the lifespan of its components. Proactive care can save you from unexpected repairs and ensure your vehicle consistently passes emissions tests.
Regular EVAP System Checks
Inspect the Gas Cap Regularly:
- Tightness Check: Make it a habit to check your gas cap for tightness every time you refuel. A loose gas cap is a frequent cause of EVAP system leaks and check engine lights.
- Condition Inspection: Examine the gas cap for signs of wear and tear, such as cracks, damage to the sealing ring, or general degradation. Replace the gas cap if any imperfections are found.
Check Hoses and Connections:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly inspect all hoses and connections within the EVAP system for signs of damage. Look for cracks, cuts, looseness, or any visible wear that could lead to leaks.
- Professional Smoke Test: Consider having a professional smoke test performed annually. This test introduces smoke into the EVAP system under pressure and can effectively pinpoint even small, hard-to-detect leaks.
Monitor the Charcoal Canister:
- Contamination Check: Ensure the charcoal canister is not contaminated with liquid fuel or water. Contamination can significantly reduce its vapor-absorbing capacity.
- Replacement Schedule: Follow the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations for inspecting and replacing the charcoal canister. Replacement is usually recommended if there are persistent fuel vapor recovery issues or after significant fuel spills or leaks.
Utilize Diagnostic Tools:
- Regular OBD2 Scans: Periodically connect your OBD2 scanner to check for any pending or active EVAP system-related codes, even if the check engine light is not illuminated. Early detection of codes can help address minor issues before they escalate.
Best Practices for EVAP System Efficiency and Longevity
Adhere to a Regular Maintenance Schedule:
- Service Intervals: Follow your vehicle manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule diligently. Routine maintenance often includes inspections of the EVAP system as part of a comprehensive vehicle checkup.
- Professional Inspections: Have your EVAP system professionally inspected, especially if you live in a hot climate where the system works harder due to increased fuel evaporation rates.
Avoid Overfilling the Fuel Tank:
- Stop at the First Click: When refueling, stop filling the tank as soon as the fuel pump nozzle clicks off for the first time. Overfilling can force liquid fuel into the charcoal canister, saturating it and reducing its efficiency, potentially leading to damage.
Educate Yourself About Your Vehicle’s EVAP System:
- Consult the Owner’s Manual: Familiarize yourself with the EVAP system components and operation as described in your vehicle’s owner’s manual. Understanding the system can help you recognize potential problems early.
Address EVAP System Repairs Promptly:
- Prioritize Repairs: If you suspect or detect an EVAP system issue, address it promptly. Delaying repairs can lead to more significant problems, including failed emissions tests, decreased fuel efficiency, and potential damage to other components.
By implementing these regular checks and best practices, you can ensure your vehicle’s EVAP system remains in optimal working condition, providing both environmental benefits and sustained vehicle performance. Consistent maintenance not only helps prevent costly repairs but also contributes to the overall longevity of your vehicle.
Conclusion: Maintaining a Healthy EVAP System with OBD2 Testing
In this comprehensive guide on using OBD2 scanners for EVAP tests, we have covered the essential functions, diagnostic procedures, and maintenance practices for ensuring the health of your vehicle’s Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system. From understanding the basics of the EVAP system and common issues to exploring the advanced capabilities of OBD2 scanners like the Foxwell NT530 and NT650 Elite, we’ve highlighted the critical role these tools play in vehicle diagnostics and environmental responsibility. Regular EVAP system testing and maintenance are not just about adhering to emission standards; they are integral to maintaining your vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does an EVAP test check in my car?
An EVAP test specifically checks for leaks and malfunctions within the Evaporative Emission Control System. It ensures that fuel vapors are properly contained and not released into the atmosphere, verifying the system’s integrity and environmental compliance.
Can I perform an EVAP test at home?
Yes, you can perform an EVAP test at home if you have an OBD2 scanner that supports EVAP system testing. Follow the scanner manufacturer’s instructions for proper test procedures and interpretation of results.
How often should I perform an EVAP test?
It is recommended to perform an EVAP test annually or whenever you notice a check engine light and suspect it might be related to an emissions issue. Regular testing can help catch minor problems before they become major repairs.