Navigating the world of car diagnostics can be confusing, especially when you encounter terms like OBD1 and OBD2. Many car owners and even some technicians find themselves asking: Can an OBD2 scanner read OBD1 systems? Understanding the differences between these onboard diagnostic systems is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and repair. This article will clarify whether OBD2 scanners are compatible with OBD1 and guide you in choosing the right diagnostic tools for your vehicle.
Decoding OBD1 and OBD2: A Diagnostic Evolution
OBD stands for On-Board Diagnostics, a system implemented in vehicles to monitor and report on various vehicle systems. Over time, OBD systems have evolved, leading to distinct generations known as OBD1 and OBD2.
OBD1: The Precursor to Standardization
OBD1 was the first generation of on-board diagnostic systems. Used predominantly in vehicles manufactured before the mid-1990s, and in some models extending up to the early 2000s, OBD1 systems were manufacturer-specific. This means that each car manufacturer often had its own diagnostic connectors, communication protocols, and trouble code definitions. Locating the diagnostic port in OBD1 vehicles could also be an adventure, sometimes found under the dashboard on the driver’s side or even within the engine bay.
OBD2: The Era of Standardization and Enhanced Data
OBD2 represents a significant leap forward. Becoming mandatory in the USA in 1996 and subsequently adopted globally, OBD2 brought standardization to vehicle diagnostics. Key improvements included:
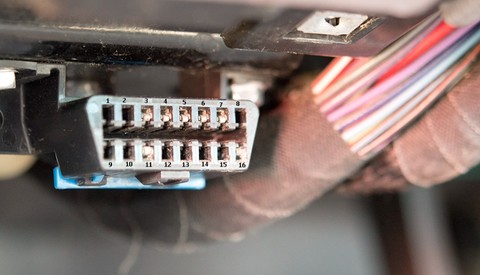
- Standardized Connector: A uniform 16-pin Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC) was introduced, making it easier to connect scan tools.
- Standardized Trouble Codes: Generic trouble codes (P-codes) were established across manufacturers, simplifying diagnosis and repair.
- Enhanced Data Parameters: OBD2 systems provide access to a wider range of vehicle data parameters, offering a more comprehensive view of vehicle health.
The Compatibility Question: Can OBD2 Scanners Read OBD1?
Now, let’s address the core question: Can an OBD2 scanner effectively read and diagnose an OBD1 system?
The straightforward answer is no. OBD2 scanners are designed to communicate using the standardized protocols and connector configurations of OBD2 systems. They are not engineered to interpret the varied and manufacturer-specific protocols of OBD1.
Why OBD2 Scanners Fail with OBD1:
- Different Communication Protocols: OBD1 systems utilize a range of manufacturer-specific communication protocols, which are fundamentally different from the standardized protocols used in OBD2.
- Connector Incompatibility: While adapters exist to physically connect an OBD2 scanner to an OBD1 port, these adapters only change the connector shape, not the communication protocol. Simply put, an adapter cannot magically make an OBD2 scanner understand OBD1 protocols.
- Lack of Software Interpretation: OBD2 scanners are programmed to interpret OBD2 diagnostic codes and data parameters. They lack the necessary software and programming to understand and translate OBD1’s unique coding and data structures.
The Adapter Myth:
It’s a common misconception that using an adapter will enable an OBD2 scanner to work on an OBD1 vehicle. This is incorrect. Adapters are merely physical connector converters. They allow you to plug an OBD2 scanner into an OBD1 port, but they do not bridge the communication gap between the two different diagnostic systems. The OBD2 scanner will still be attempting to communicate using OBD2 protocols, which the OBD1 system will not understand.
Identifying Your Vehicle’s OBD System
Determining whether your vehicle is OBD1 or OBD2 is crucial for selecting the correct diagnostic tools. Here are some guidelines:
- Manufacturing Year: As a general rule, vehicles manufactured before 1996 are typically OBD1. Vehicles manufactured in 1996 and later are usually OBD2. However, there can be exceptions. Some manufacturers began transitioning to OBD2 as early as 1994 or 1995.
- Check Your Vehicle’s Manual: Your vehicle’s owner’s manual is the definitive source of information. It should specify the OBD standard your vehicle complies with.
- Inspect the Diagnostic Port:
- OBD2 Port: A standardized 16-pin DLC, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. This port is typically trapezoidal in shape.
- OBD1 Ports: OBD1 ports are non-standardized and vary in shape and pin configuration. They can be found in various locations, including under the dash or in the engine bay. Examples include 14-pin Nissan connectors and 22-pin Toyota connectors.
Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tools for OBD1 Vehicles
If you own an OBD1 vehicle, you’ll need to use diagnostic tools specifically designed for OBD1 systems. These tools are equipped to handle the manufacturer-specific protocols and connector types of older vehicles.
OBD1 Scan Tools:
- Specialized OBD1 Scanners: These scanners are designed to communicate with OBD1 systems and often come with adapters for various OBD1 connector types.
- Professional-Grade Scan Tools: Some advanced professional scan tools are backward-compatible and can diagnose both OBD1 and OBD2 vehicles. These are typically more expensive but offer wider vehicle coverage and functionality.
See our range of OBD1 scan tools here
OBD1 Adapters:
For OBD1 vehicles, you may require adapter cables to connect your OBD1 scan tool to the vehicle’s diagnostic port. These adapters bridge the physical connector difference.
We supply a range of OBD1 adapter cabler here
Conclusion: OBD2 and OBD1 are Incompatible Systems
In conclusion, OBD2 scanners cannot read OBD1 systems. They are fundamentally different in terms of communication protocols, connector types, and diagnostic code interpretation. Attempting to use an OBD2 scanner on an OBD1 vehicle, even with an adapter, will not yield accurate diagnostic information.
To effectively diagnose and repair OBD1 vehicles, it is essential to use OBD1-compatible scan tools and appropriate adapters. Always verify your vehicle’s OBD standard to ensure you are using the correct diagnostic equipment. Understanding these distinctions will save you time, frustration, and ensure accurate vehicle diagnostics.