Experiencing trouble connecting to your OBD2 port can be frustrating, especially when you need to run diagnostics or pass a smog check. Like many, you might find yourself scratching your head when your trusty OBD2 scanner, such as a BAFX Products OBDII Diagnostic Interface, suddenly refuses to link up with your vehicle’s computer. This was the exact scenario faced by a Toyota Tacoma owner, and their journey to resolution offers valuable insights into diagnosing and fixing OBD2 connection problems.
Initially, the owner of a 2012 Toyota Tacoma TRD Sport encountered a roadblock at the smog check station. The testing computer failed to connect to their truck’s OBD2 port, preventing the necessary emissions test. Further investigation at home revealed that their BAFX OBDII scanner, indicated by a single red light and no Bluetooth connection, was also unable to establish a link.
Common online advice points towards potential issues like wiring problems, a blown fuse, or even a faulty ECU (Engine Control Unit). However, the solution in this case turned out to be simpler and involved using a powered scan tool.
Step-by-Step OBD2 Port Troubleshooting
Here’s a breakdown of troubleshooting steps, drawing from the Tacoma owner’s experience and general best practices:
1. Verify Your Scan Tool and Cable
The first step is to rule out any issues with your diagnostic equipment itself. A faulty scan tool or cable can easily lead to connection failures.
- Test with a different scanner: Try using a different OBD2 scanner to see if it connects. Smog shops, auto parts stores, and dealerships typically have professional-grade scanners you can test with.
- Inspect your cable: If your scanner uses a cable, carefully inspect it for any damage, such as frayed wires or bent connectors. In some cases, like the user mentioned regarding a Scangauge cable, the cable itself might be the problem.
2. Check the OBD Fuse
A blown fuse is a common cause of OBD2 port malfunctions. The OBD port is typically powered by a dedicated fuse.
- Locate the OBD fuse: For Toyota Tacomas (and many other vehicles), the OBD fuse is often located in the engine bay fuse box, on the driver’s side. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the precise location and fuse number. In the Tacoma’s case, it was fuse #7.
- Inspect the fuse: Visually inspect the fuse to see if the internal wire is broken or melted. You can also use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity.
- Fuse Amperage: The Tacoma owner noted that the OBD fuse was a 7.5 amp fuse. Some online discussions mention a 20A EFI fuse, but a blown EFI fuse would likely cause more significant vehicle issues. Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating.
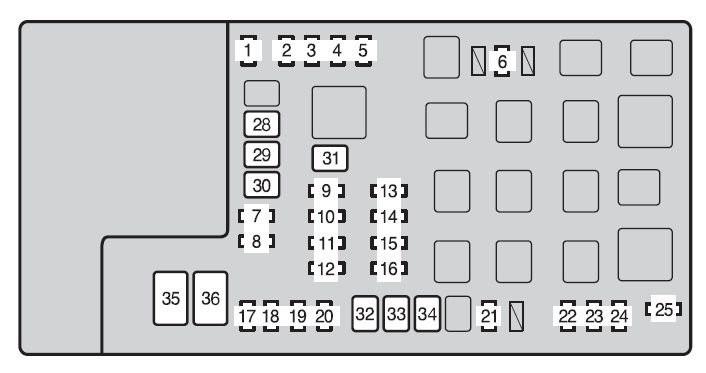 Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
3. Examine the Wiring
If the fuse is intact, the next step is to check the wiring between the OBD port, fuse box, and ECU.
- Visual inspection: Carefully inspect the wiring harness for any signs of damage, such as cuts, abrasions, or corrosion. Pay close attention to the wiring around the OBD port itself.
- Professional wiring check: If you’re not comfortable inspecting wiring yourself, or if you suspect a more complex wiring issue, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic.
4. Battery Reset
Sometimes, a simple system reset can resolve communication glitches.
- Disconnect the battery: Disconnect the negative battery terminal for about 30 seconds, then reconnect it. This can sometimes clear temporary electrical issues that might be affecting the OBD2 port.
5. Try a Powered OBD Scanner
This was the key to resolving the Tacoma owner’s problem.
- Powered vs. Unpowered Scanners: Most basic OBD2 scanners, like the BAFX Bluetooth dongle, are “unpowered.” They rely on power supplied by the vehicle’s OBD2 port. “Powered” scanners, on the other hand, have their own internal batteries or an external power source.
- The Solution: Using a powered scan tool, the Toyota dealership technician was able to connect to the Tacoma’s OBD2 port. This suggests that the issue wasn’t a complete lack of power to the port, but perhaps a weak or insufficient power supply that the unpowered BAFX scanner couldn’t utilize, while the powered scanner overcame this limitation.
6. ECU as a Last Resort
A faulty ECU is a less common but possible cause of OBD2 port problems.
- Consider ECU issues after other steps: If all other troubleshooting steps fail, a problem with the ECU might be considered. However, ECU issues are typically more complex and often accompanied by other symptoms.
Conclusion: Power Supply and OBD2 Port Functionality
The experience of the Toyota Tacoma owner highlights the importance of considering the OBD2 port’s power supply when troubleshooting connection issues. While the exact reason why non-powered scanners stopped working in this case remains unclear, the powered scan tool provided a practical solution.
It’s worth noting that OBD2 ports have specific pins designated for power supply. Further investigation into these pins and potential power delivery problems could shed more light on such scenarios. If you encounter similar OBD2 connection problems, especially after ruling out basic issues like fuses and scanner malfunctions, trying a powered OBD2 scan tool might be the key to unlocking your vehicle’s diagnostic data. And while you’re at it, maybe give your BAFX scanner a closer look – is the sticker peeling off? While seemingly unrelated, paying attention to details, even cosmetic ones, can sometimes lead you to unexpected insights during troubleshooting.