The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port in your 2014 Toyota Tacoma Prerunner V6 is a crucial interface for accessing your vehicle’s computer system. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast checking engine codes or a professional technician diagnosing complex issues, knowing the OBD2 port location and how to troubleshoot potential problems is essential. This article will guide you to find your OBD2 port and provide troubleshooting steps if you encounter connectivity issues.
Locating the OBD2 Port in Your 2014 Toyota Tacoma Prerunner V6
For the 2014 Toyota Tacoma Prerunner V6, the OBD2 port is typically located inside the cabin on the driver’s side. Specifically, you’ll usually find it beneath the dashboard, near the steering column. It’s often positioned close to the center console area or slightly to the left, above the pedals. You might need to crouch down and look under the dash to spot it. The port is a trapezoid-shaped, 16-pin connector, making it easily recognizable.
[paragraph break]
Once located, you can connect a compatible OBD2 scanner or code reader to access your Tacoma’s diagnostic information. This port allows you to read trouble codes, monitor engine performance, and perform various diagnostic tests, making it an invaluable tool for vehicle maintenance and repair.
Troubleshooting OBD2 Port Connection Issues
Sometimes, you might encounter issues when trying to connect to your OBD2 port. If your scanner fails to establish a connection, here are some troubleshooting steps you can take, drawing from common experiences and potential problems:
1. Verify Your Scan Tool and Cable:
The first step is to ensure that your scan tool and its cable are functioning correctly. Just like the original poster’s experience, a faulty cable or scanner can be the culprit.
- Test with a different scanner: If possible, try using a different OBD2 scanner to see if the issue persists. Borrowing one from a friend or trying one at an auto parts store can help isolate the problem.
- Inspect the cable: Check the OBD2 cable for any visible damage, such as frayed wires or bent pins. A damaged cable can prevent proper communication.
2. Check the OBD Fuse:
A blown fuse is a common reason for a non-functional OBD2 port. The OBD2 system is protected by a fuse, and if this fuse blows, the port will lose power.
- Locate the fuse box: For a 2014 Toyota Tacoma, the fuse box you need to check is typically located in the engine bay on the driver’s side, similar to the 2012 model mentioned in the original post. Refer to your owner’s manual for the exact location of the fuse box diagram.
- Identify the OBD fuse: Consult the fuse box diagram (usually printed on the fuse box cover) to find the fuse associated with the OBD or diagnostic system. In many Toyota models of this era, it’s often a 7.5 amp or 10 amp fuse. The original post mentioned Fuse #7 (7.5 amp) in the engine bay for a 2012 model, this is a good starting point to verify for the 2014 as well, but always double-check your specific vehicle’s fuse diagram.
- Check and replace the fuse: Visually inspect the fuse to see if the wire inside is broken or melted. If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage.
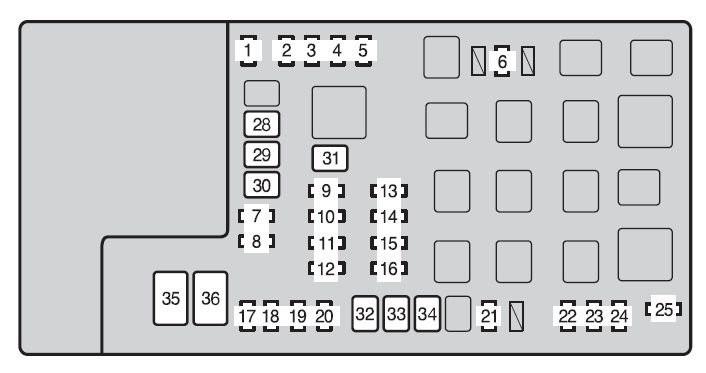 Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
3. Inspect Wiring (Advanced):
If the fuse is not the issue, the problem might lie in the wiring between the OBD2 port, the fuse box, and the Engine Control Unit (ECU). This step requires more advanced knowledge and potentially specialized tools.
- Visual inspection: Carefully inspect the wiring around the OBD2 port and leading to the fuse box for any signs of damage, such as cuts, frays, or corrosion.
- Continuity testing: Using a multimeter, you can perform continuity tests on the wires to check for breaks or shorts. You’ll need the wiring diagram for your 2014 Toyota Tacoma to perform this accurately. This is generally recommended for experienced DIYers or professional technicians.
4. Try a Powered OBD2 Scanner:
As highlighted in the original story, using a powered OBD2 scanner can sometimes bypass power delivery issues with the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Powered vs. Unpowered Scanners: Most basic OBD2 scanners rely on power from the vehicle’s OBD2 port. However, some scanners are powered, either by batteries or an external power source.
- The Fix in the Story: The original poster found that a powered scan tool worked when a non-powered one didn’t. This suggests a potential issue with the power supply to the OBD2 port in their Tacoma.
- Consider a Powered Scanner: If you’re consistently having trouble with non-powered scanners, trying a powered OBD2 scanner is a worthwhile step.
5. Disconnect and Reconnect Battery:
Sometimes, a simple system reset can resolve communication glitches.
- Battery Disconnect: Disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for about 30 seconds and then reconnecting it can reset the ECU and other electronic modules. This is a general troubleshooting step that can sometimes resolve minor electrical issues.
6. ECU Issues (Less Likely, More Serious):
While less common, a malfunctioning ECU could be the reason for OBD2 port problems. However, ECU issues often manifest in other symptoms as well, such as engine performance problems or warning lights.
- Consider Professional Diagnosis: If you’ve exhausted the simpler troubleshooting steps and still have OBD2 port issues, it’s advisable to seek professional diagnosis from a qualified mechanic or Toyota dealership. They have advanced diagnostic tools and expertise to pinpoint more complex problems, including potential ECU faults.
Personal Experience and Takeaway:
The original poster’s experience with their 2012 Tacoma TRD Sport provides valuable real-world insight. Leaving a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner plugged in long-term might have contributed to a drain or issue, although this is speculative. The key takeaway from their story is the successful use of a powered scan tool when unpowered ones failed. This suggests that in some cases, the OBD2 port might have a power delivery problem, even if the fuse is intact. The Toyota dealership’s use of a battery-equipped scan tool and the eventual resolution after a recall service further underscores the complexity of diagnosing these issues.
Conclusion:
Finding the OBD2 port on your 2014 Toyota Tacoma Prerunner V6 is usually straightforward. It’s typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. If you encounter connection problems, start with simple checks like the fuse and try a powered scan tool. While wiring or ECU issues are possible, they are less frequent. By following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively diagnose and potentially resolve OBD2 port issues on your 2014 Toyota Tacoma Prerunner V6, ensuring you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.

