The OBD2 port in your 2nd gen Toyota Tacoma is a crucial access point for diagnostics and smog checks. If you’re experiencing issues connecting to it, you’re not alone. A non-functional OBD2 port can prevent you from reading trouble codes, using scan tools, and even passing emissions tests. This guide will walk you through common problems and troubleshooting steps for your 2nd Gen Tacoma Obd2 Port, helping you get back on the road to diagnostics and repairs.
Common OBD2 Port Problems in 2nd Gen Tacoma
Several factors can contribute to a malfunctioning OBD2 port in your 2nd Gen Tacoma. Let’s explore the most frequent culprits:
- Blown Fuse: This is often the simplest and most common reason for a dead OBD2 port. A fuse protects the circuit, and an overload can cause it to blow, interrupting power to the port.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring can prevent proper communication. This could be due to wear and tear, rodent damage, or previous modifications.
- ECU Problems: In rare cases, a faulty Engine Control Unit (ECU) might be the reason your OBD2 port isn’t working. The ECU is the computer that manages your engine and communicates through the OBD2 port.
- Scan Tool Compatibility or Power Issues: Sometimes, the problem isn’t with your Tacoma, but with the scan tool itself. Some basic scan tools may not be compatible, or the port might not be providing enough power for certain scanners to operate correctly.
Troubleshooting Steps for Your 2nd Gen Tacoma OBD2 Port
Before assuming the worst, follow these troubleshooting steps to pinpoint the issue with your 2nd gen Tacoma OBD2 port:
-
Check Your Scan Tool: The first step is to rule out a problem with your scan tool. Try using your scan tool on another vehicle to confirm it’s working correctly. If possible, test with a different scan tool on your Tacoma. Smog shops, auto parts stores, or dealerships usually have professional-grade scanners you can test with. A faulty cable can also be the issue if your scan tool uses one.
-
Inspect the OBD Fuse: Locate the OBD fuse in your Tacoma’s engine bay fuse box. For a 2nd gen Tacoma, this is typically fuse #7 (7.5 amp) in the engine compartment fuse box on the driver’s side. Refer to your owner’s manual for the exact location if needed. Visually inspect the fuse to see if the filament is broken. Replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Note: Some online forums mention fuse #19 (20A EFI fuse), but if this fuse is blown, you’ll likely have more significant engine management issues beyond just the OBD2 port.
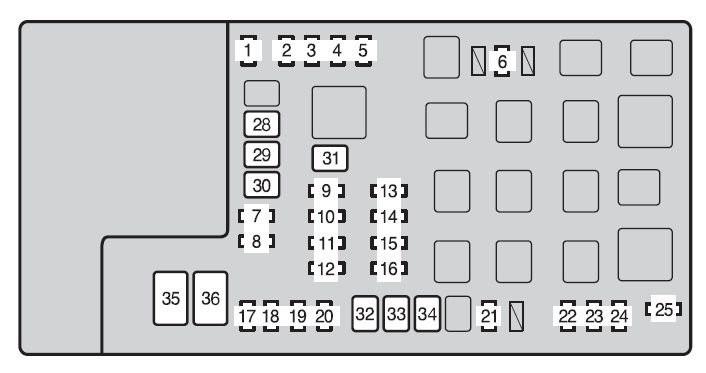 Engine compartment fuse box location in a 2012 2nd Gen Toyota Tacoma, highlighting the typical area for fuse #7.
Engine compartment fuse box location in a 2012 2nd Gen Toyota Tacoma, highlighting the typical area for fuse #7. -
Examine the Wiring: Visually inspect the wiring around the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, such as cuts, frays, or corrosion. Trace the wiring back towards the fuse box and ECU if possible, looking for any breaks or loose connections. This might require a more detailed inspection, potentially needing a mechanic if wiring issues are suspected deeper in the system.
-
Battery Reset: A simple reset can sometimes resolve communication glitches. Disconnect the negative battery terminal for about 30 seconds, then reconnect it. This can sometimes clear temporary electrical issues.
-
Try a Powered OBD2 Scanner: If standard scan tools fail, consider using a powered OBD2 scanner. These scanners have their own internal battery and supply power to the OBD2 port, bypassing any potential power delivery problems from your Tacoma. This is a common fix when the OBD2 port isn’t providing enough power.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Powered OBD2 Scanner
Using a powered OBD2 scanner is straightforward and can often resolve connectivity issues:
- Obtain a Powered Scanner: You can purchase powered OBD2 scanners online or at auto parts stores. Some professional-grade scanners used by mechanics and smog shops are also powered.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the powered OBD2 scanner into your Tacoma’s OBD2 port, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Power On: Turn on the powered scanner. It should power up using its internal battery.
- Run Diagnostics: Follow the scanner’s instructions to initiate a scan and read diagnostic codes.
Real-World Case: Solving OBD2 Port Issues with a Powered Scanner
One Tacoma owner experienced a similar OBD2 port problem when their standard Bluetooth OBD2 scanner stopped working. After troubleshooting fuses and wiring, a Toyota dealership technician discovered that their handheld ScanTool, which was battery-powered, could connect to the Tacoma’s OBD2 port without issue. It turned out that the dealership’s smog machine also had an optional battery power port, and when used, it successfully connected and completed the smog check. The solution in this case was using a powered scan tool, suggesting a potential power delivery issue within the Tacoma’s OBD2 port system that was preventing unpowered scanners from functioning correctly.
Why a Powered Scanner Might Be Necessary
While the exact reason why some 2nd gen Tacomas might have issues powering standard OBD2 scanners isn’t always clear, it could be related to a slight voltage drop or resistance in the OBD2 port’s power supply circuit over time. A powered scanner overcomes this by providing its own stable power source, ensuring reliable communication even if the vehicle’s OBD2 port power is weak.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting your 2nd gen Tacoma OBD2 port doesn’t have to be daunting. By systematically checking the fuse, wiring, and trying a powered scan tool, you can often diagnose and resolve the issue. Starting with the simple fuse check and progressing to a powered scanner can save you time and potentially expensive trips to the mechanic. If these steps don’t resolve the problem, further diagnosis by a qualified technician might be necessary to investigate potential ECU or deeper wiring harness issues.