For BMW enthusiasts and owners, particularly those who cherish the E39 5 Series, understanding your vehicle’s diagnostic systems is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting. A key component of modern vehicle diagnostics is the On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port. If you’re working on a 1996-2003 BMW E39 and need to access your car’s computer system, knowing the Bmw E39 Obd2 Location is the first step. This article will guide you to find the OBD2 port in your E39 and offer some insights into troubleshooting common communication issues.
Locating the OBD2 Port in Your BMW E39
The OBD2 port in the BMW E39 is designed for easy access, typically situated inside the cabin. You can find the BMW E39 OBD2 location in the driver’s side footwell.
- Detailed Location: Look towards the left side of the dashboard, specifically above the dead pedal and at the very end of the left side of the dashboard. You might need to crouch down and look upwards in the driver’s footwell to spot it.
- Connector Type: The OBD2 port in your E39 will be a 16-pin connector. This is the standard OBD2 connector type, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of scan tools and diagnostic equipment.
Once you’ve located the port, you can connect an OBD2 scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor live data, and perform various diagnostic tests.
Understanding the Diagnostic Connectors: OBD2 and 20-Pin
While the 16-pin OBD2 port is the primary diagnostic interface, some BMW E39 models, especially earlier ones, may also feature a 20-pin Data Link Connector.
- 20-Pin Connector: This connector is typically found under the hood, near the front right strut tower. It’s a circular connector with 20 pins. This port was more common in older BMWs and served as a diagnostic interface before OBD2 became standard.
- OBD2 as the Standard: For most diagnostic purposes, especially with modern scan tools, the 16-pin OBD2 port is the one you’ll primarily use on your BMW E39. It provides access to essential systems and modules as mandated by OBD2 standards.
Troubleshooting OBD2 Communication Issues on a BMW E39
Encountering problems communicating with your BMW E39’s computer via the OBD2 port can be frustrating. Here are troubleshooting steps, inspired by a real-world scenario on a 1999 BMW 528i (E39):
Scenario: A 1999 BMW 528i with a 2.8L engine experienced a misfire, and attempts to communicate with any module using OBD2 scan tools through both the 16-pin and 20-pin connectors failed.
Troubleshooting Steps Taken:
- Fuse Check: The first step is always to check the fuses. Inspect all fuses in the glove box and the trunk’s rear power distribution box. Ensure none are blown, as a faulty fuse can cut power to the OBD2 port or related modules.
- Scan Tool Compatibility: Try multiple OBD2 scan tools. Sometimes, compatibility issues can arise with specific scanners. Testing with different tools helps rule out scanner-related problems. In the example case, three different OBD2 scan tools were tested without success.
- 20-Pin Connector Test: If OBD2 communication fails, testing the 20-pin connector can be informative, especially on older vehicles. However, in this case, communication also failed with a Mac Mentor (generation 3) scan tool via the 20-pin connector.
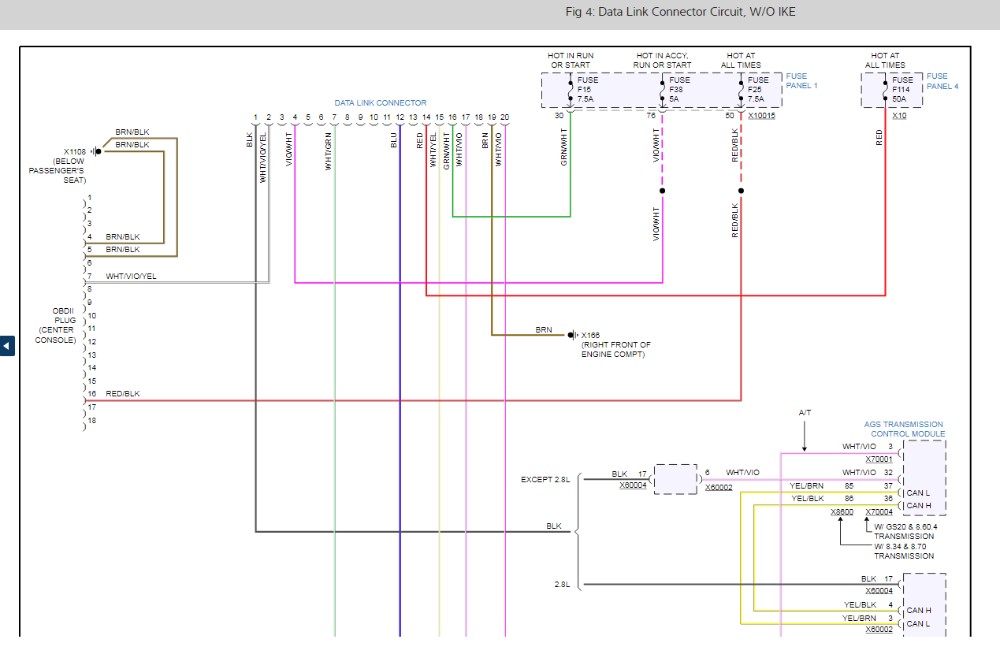
- Power at the Connector: Verify power at the diagnostic connectors. For the 20-pin connector, check for 12V at pin 2. In the example, 12V was present for a short period (10 seconds) upon starting the car, then dropped to 0V, which could indicate a power supply issue or a module shutting down communication.
- BUS System Inspection: Investigate the BUS communication systems. The example case involved scoping the CAN bus (between the transmission control module and DME) at the DME (Digital Motor Electronics) connector (X60002). Normal CAN bus signals were observed, suggesting the CAN bus itself was likely functioning.
- D-Bus Voltage Check: Check the voltage on the diagnostic bus (D-bus) pin (pin 7) of the OBD2 connector. In the example, 12V was present at idle. Voltage fluctuations were observed when a scan tool attempted to communicate, but communication still failed.
- Module Isolation (IKE Disconnection): In some BMW systems, the instrument cluster (IKE) acts as a gateway module. Disconnecting the IKE can sometimes resolve communication issues if the IKE is faulty. This was attempted in the example case, but communication with the DME still failed.
Suspected Cause: Based on these troubleshooting steps, particularly the consistent communication failure and voltage behavior, a likely cause in the example scenario is a faulty DME (engine control module) itself. If all basic checks pass and communication remains impossible, the DME may need replacement or further in-depth diagnostics.
Conclusion
Locating the BMW E39 OBD2 location is straightforward, typically in the driver’s side footwell. Understanding both the OBD2 and 20-pin connectors is helpful for BMW E39 diagnostics. If you encounter OBD2 communication problems, systematic troubleshooting, including fuse checks, scan tool testing, power and BUS system inspections, is essential. In complex cases, a faulty DME or other module may be the underlying issue, potentially requiring professional diagnosis and repair. Always consult a repair manual specific to your BMW E39 model year for detailed procedures and safety information.