When your 2009 Dodge Journey is experiencing engine overheating, especially in scenarios where the radiator fan’s operation is in question, checking the OBD2 system and related fuses can be a crucial step in the diagnostic process. While the original issue might point towards fan relays and circuits, ensuring the integrity of the OBD2 system’s fuse is fundamental, as this system is often used to read diagnostic codes related to cooling and fan operation.
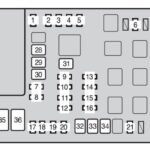
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is essential for retrieving trouble codes and monitoring vehicle systems. If there’s a blown fuse affecting the OBD2 system, it may hinder your ability to use a scan tool to properly diagnose fan issues, among other problems. Locating the fuse box in your 2009 Dodge Journey, usually found in the interior or engine compartment, and consulting your owner’s manual for the specific OBD2 fuse location is the first step.
It’s important to understand that while there may not be a fuse labeled explicitly as “OBD2 fuse”, several fuses can impact the functionality of the OBD2 port and related systems. These could include fuses for the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or the Transmission Control Module (TCM), which are integral to engine and cooling fan management. A problem with these fuses could indirectly affect fan operation or the ability to diagnose fan issues through the OBD2 port.
If you are attempting to diagnose a radiator fan problem, and especially if you are trying to use a scan tool via the OBD2 port to activate the fan relays as a test, a faulty fuse could be the simplest point of failure. Before diving into more complex diagnostics like relays or the fan motor itself, a quick check of the relevant fuses for the OBD2 system and engine control modules is highly recommended. Refer to your 2009 Dodge Journey fuse diagram to identify and inspect the fuses related to the PCM, TCM, and potentially labeled as “diagnostic port” or similar, ensuring they are in good condition. This initial step can save time and effort in pinpointing the root cause of fan and diagnostic communication problems.