Fuses are essential components in your 2006 Ford Ranger, protecting its electrical system from damage due to overloads. If you’re experiencing issues with your vehicle’s electronics, such as a malfunctioning OBD2 port, checking the fuses should be one of your first steps. This guide will specifically address the 2006 Ford Ranger Obd2 Fuse, providing you with the necessary information to locate it, understand its function, and troubleshoot potential problems.
The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is crucial for vehicle diagnostics, allowing mechanics and DIY enthusiasts to read trouble codes and assess the health of your Ford Ranger’s engine and other systems. If your OBD2 scanner isn’t powering up or connecting properly, a blown fuse could be the culprit.
This article will guide you through the fuse locations in your 2006 Ford Ranger, pinpointing the fuse related to the OBD2 port and the diagnostic connector. We’ll also cover how to check and replace fuses, ensuring you can get your diagnostic port back online and troubleshoot any electrical issues effectively.
Understanding Fuse Locations in Your 2006 Ford Ranger
Your 2006 Ford Ranger has two main fuse box locations:
- Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel: Located inside the vehicle, this panel is usually more accessible and houses fuses for interior and some essential vehicle functions.
- Power Distribution Box: Situated in the engine compartment, this box contains fuses and relays for high-power systems and engine-related components.
To find the specific fuse for your OBD2 port, you’ll primarily need to focus on the Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel.
Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel Diagram and OBD2 Fuse Location
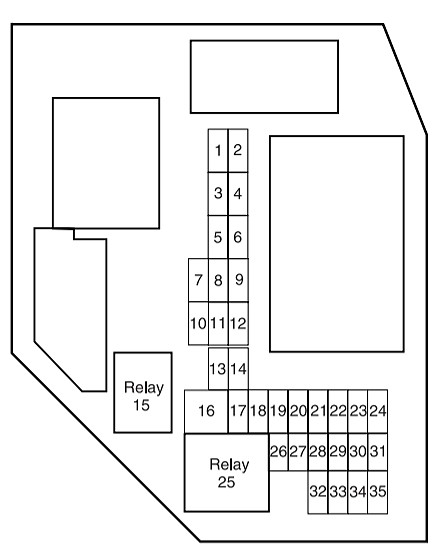
The passenger compartment fuse panel in your 2006 Ford Ranger is located on the left end of the instrument panel. To access it, you’ll need to remove the fuse panel cover. You can typically do this by inserting your finger into the provided divot and gently pulling the cover off.
Once you’ve accessed the fuse panel, you can refer to the fuse diagram, often found on the inside of the fuse panel cover itself. This diagram will illustrate the location of each fuse and relay, along with its corresponding function and amperage rating.
According to the fuse chart for the passenger compartment fuse panel of a 2006 Ford Ranger, the OBD II port, also known as the diagnostic connector, is protected by fuse number 29.
| No. | AMPS | Protected circuits |
|---|---|---|
| … | … | … |
| 29 | 20 | Cigar lighter or power point, Diagnostic connector (OBD II) |
| … | … | … |


Fuse number 29 is a 20 amp fuse and is also responsible for the cigar lighter or power point. If both your OBD2 port and the cigar lighter are not working, it’s highly likely that this fuse has blown.
Power Distribution Box and Related Fuses
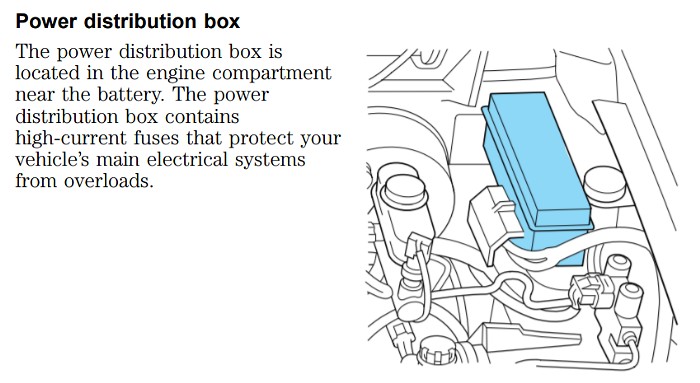
While the primary fuse for the OBD2 port is in the passenger compartment, the Power Distribution Box in the engine compartment plays a crucial role in supplying power to various systems, including the passenger compartment fuse panel itself.
The power distribution box is located in the engine compartment on the driver’s side, near the fender. It houses higher amperage fuses and relays that protect major electrical circuits.
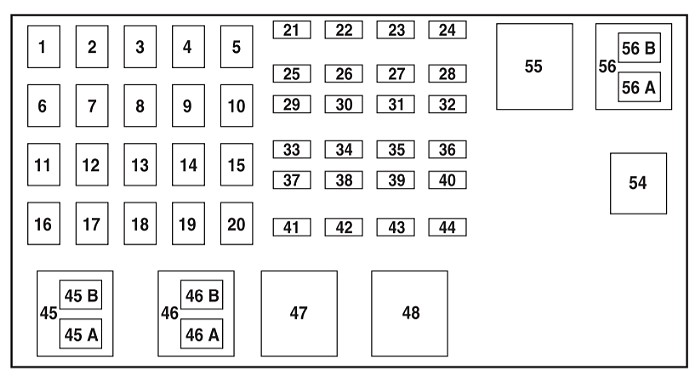
While there isn’t a specific fuse in the power distribution box directly labeled “OBD2 fuse,” it’s important to note that the passenger compartment fuse panel itself receives power from the power distribution box. Fuses 1, 3 and 5 (depending on the year and chart variations) in the power distribution box, which are high amperage fuses (50A or 40A), supply power to the passenger compartment fuse panel. If there’s a major power issue affecting multiple systems in the passenger compartment, it’s worth checking these larger fuses in the power distribution box as well. However, for a localized issue specifically with the OBD2 port, fuse #29 in the passenger compartment is the primary suspect.
| No. | AMP | Protected circuits |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 / 40 | Passenger compartment fuse panel |
| 3 | 50 / 40 | Passenger compartment fuse panel |
| 5 | 50 | Passenger compartment fuse panel |
| … | … | … |
Checking and Replacing the 2006 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse
Once you’ve located fuse #29 in the passenger compartment fuse panel, you need to check if it’s blown. Here’s how:
-
Access the Fuse Panel: As described earlier, open the passenger compartment fuse panel.
-
Locate Fuse #29: Refer to the fuse diagram to pinpoint fuse number 29.
-
Visually Inspect the Fuse: Look at the fuse. Most fuses are transparent, allowing you to see the internal wire. If the wire inside is broken or melted, the fuse is blown and needs replacement.
-
Fuse Tester (Optional but Recommended): For a more definitive check, use a fuse tester. These inexpensive tools can test a fuse without removing it. Simply align the tester prongs with the metal contacts on top of the fuse and check for the indicator light. If the light doesn’t illuminate, the fuse is blown.
-
Remove the Blown Fuse: If the fuse is blown, use the fuse pulling tool (often found in the fuse panel itself or the power distribution box) to carefully remove it.
-
Replace with the Correct Fuse: Crucially, replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating (20 amp in this case). Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can overload the circuit and cause serious damage, potentially leading to a fire.
-
Install the New Fuse: Push the new 20 amp fuse firmly into the fuse slot.
-
Replace the Fuse Panel Cover: Snap the fuse panel cover back into place.
-
Test the OBD2 Port: Try using your OBD2 scanner again to see if it now powers up and connects. Also, check if your cigar lighter or power point is working again.
Troubleshooting Persistent Fuse Issues
If the 2006 Ford Ranger OBD2 fuse blows repeatedly after replacement, it indicates an underlying electrical problem in the circuit. This could be due to:
- Short Circuit: A bare wire or component fault causing excessive current draw.
- Overload: Too many devices drawing power from the same circuit.
- Faulty Component: A malfunctioning OBD2 port or related wiring.
In such cases, further electrical diagnosis is necessary. It’s recommended to consult a qualified mechanic to identify and repair the root cause of the fuse blowing to prevent further damage to your vehicle’s electrical system.
By following these steps, you should be able to effectively locate, check, and replace the 2006 Ford Ranger OBD2 fuse, restoring functionality to your diagnostic port and addressing common electrical issues. Remember to always prioritize safety and use the correct replacement fuses for your vehicle.