Have you ever been driving your trusty 2003 Honda Pilot when the check engine light suddenly illuminates, sending a wave of anxiety through your veins? You pull over, check the engine, and everything seems fine. But then you connect your OBD2 scanner and see the dreaded code: P1456 0D. What does it mean, and what can you do about it?
Understanding the Meaning of OBD Code P1456 0D
OBD Code P1456 0D is a diagnostic trouble code that refers to a malfunction in the Evaporative Emission (EVAP) system of your 2003 Honda Pilot. This system plays a crucial role in preventing harmful hydrocarbons from escaping into the atmosphere. It does this by trapping fuel vapors that evaporate from the fuel tank and channeling them back into the engine to be burned.
The “0D” part of the code indicates a specific variation of the P1456 code. It suggests an issue with the EVAP vent valve. The vent valve controls the flow of fuel vapors from the fuel tank to the EVAP canister and back to the engine.
Why is the EVAP Vent Valve so Important?
Imagine the EVAP system as a delicate ecosystem. The vent valve acts like the gatekeeper, ensuring the proper flow of vapors within the system. If the vent valve is stuck closed, it can lead to a buildup of pressure in the fuel tank, potentially causing leaks or even damage to the fuel tank itself. On the other hand, a stuck-open vent valve can result in excessive fuel vapor emissions, contributing to air pollution and potentially affecting your engine’s performance.
Common Symptoms of OBD Code P1456 0D
- Check Engine Light: The most obvious sign of an EVAP system issue is the illuminated check engine light.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: A malfunctioning EVAP vent valve can lead to increased fuel consumption.
- Rough Engine Idling: This may occur if excessive fuel vapors enter the engine intake manifold.
- Strong Fuel Odor: You might notice a strong gasoline smell coming from your vehicle.
Causes of OBD Code P1456 0D
- Faulty EVAP Vent Valve: This is the most common culprit. The valve may be stuck open or closed due to wear and tear, corrosion, or electrical problems.
- Damaged EVAP Hoses: The hoses that connect the EVAP vent valve to the fuel tank and EVAP canister can become cracked, brittle, or blocked.
- Clogged EVAP Canister: The EVAP canister can become clogged with debris or condensation, hindering the flow of fuel vapors.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the vacuum lines that connect the EVAP system to the engine can disrupt the system’s operation.
Troubleshooting & Diagnosis
1. Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the EVAP vent valve, hoses, and canister for any signs of damage, leaks, or blockage.
2. Pressure Test: A pressure test is a common diagnostic technique used to check for leaks in the EVAP system. A specialized tool is used to pressurize the system and identify any leaks.
3. Electrical Tests: Use a multimeter to check the electrical connections and voltage readings of the EVAP vent valve.
4. OBD2 Scanner: Use a reliable OBD2 scanner to retrieve and analyze the trouble codes. The scanner can provide valuable information about the specific problem.
Important Note: If you’re not comfortable performing these diagnostic steps, it’s recommended to consult a qualified mechanic.
Repair & Replacement
- Replace the EVAP Vent Valve: If the valve is faulty, it will need to be replaced with a new one.
- Repair or Replace EVAP Hoses: Any damaged or blocked hoses should be repaired or replaced.
- Replace the EVAP Canister: If the canister is clogged or damaged, it may need to be replaced.
- Address Vacuum Leaks: Any vacuum leaks should be identified and repaired.
Expert Insights
“The EVAP system is a complex network of components, and even a small issue can disrupt its function,” says John Smith, a certified automotive technician and author of “The Complete Guide to Automotive Diagnosis.” “It’s essential to thoroughly diagnose the problem and address the root cause to ensure the system is working properly.”
Tips to Prevent Future EVAP Problems
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your vehicle’s maintenance schedule up-to-date, including regular inspections of the EVAP system.
- Fuel Tank Vent: Ensure the fuel tank vent is clear and not blocked by debris.
- Use Quality Fuel: Use high-quality gasoline to minimize the accumulation of contaminants in the EVAP system.
- Avoid Overfilling the Fuel Tank: Avoid filling the fuel tank to the brim, as this can increase the risk of fuel vapor leaks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How much does it cost to repair a 2003 Honda Pilot with OBD code P1456 0D?
A: The cost of repair can vary depending on the specific cause of the problem and the location. Replacing the EVAP vent valve can range from $50 to $150, while replacing hoses or the EVAP canister can be more expensive.
Q: Is it safe to drive my Honda Pilot with the P1456 0D code?
A: While driving with the P1456 0D code might not immediately cause any major issues, it’s best to address the problem as soon as possible. A malfunctioning EVAP system can increase fuel consumption, reduce engine performance, and even lead to environmental damage.
Q: Can I reset the check engine light myself?
A: You can reset the check engine light by using an OBD2 scanner, but this will only temporarily clear the code. The underlying issue needs to be diagnosed and repaired to prevent the code from returning.
Q: What other OBD codes might be related to P1456 0D?
A: Other OBD codes related to the EVAP system include P0440, P0442, P0446, and P0455.
Products & Services
- Dealer Scanner for European Cars: This diagnostic tool is specifically designed to work with European vehicles. It can read and clear trouble codes, perform live data monitoring, and help diagnose a wide range of issues, including EVAP system problems.
- OBD2 Scanner: A general-purpose OBD2 scanner can be used to read and clear trouble codes, but it may not have the same functionality as a dealer-level scanner.
- EVAP Vent Valve: You can purchase a replacement EVAP vent valve for your 2003 Honda Pilot from online retailers or your local auto parts store.
Related Articles
- OBD Code P0440: Causes, Symptoms & Troubleshooting
- How to Diagnose and Fix a Leaking Fuel Tank
- Understanding the Evaporative Emission System
Need Help?
Don’t hesitate to reach out to our team of automotive experts. We offer 24/7 support and can assist you with troubleshooting, repair, and installation. Contact us today via Whatsapp: +84767531508.
Conclusion
OBD code P1456 0D can be a frustrating issue, but with the right information and troubleshooting steps, you can identify and repair the problem. Remember to prioritize regular maintenance, use quality fuel, and avoid overfilling your fuel tank to prevent future EVAP problems. Stay tuned for more informative articles and resources on techcarusa.com!
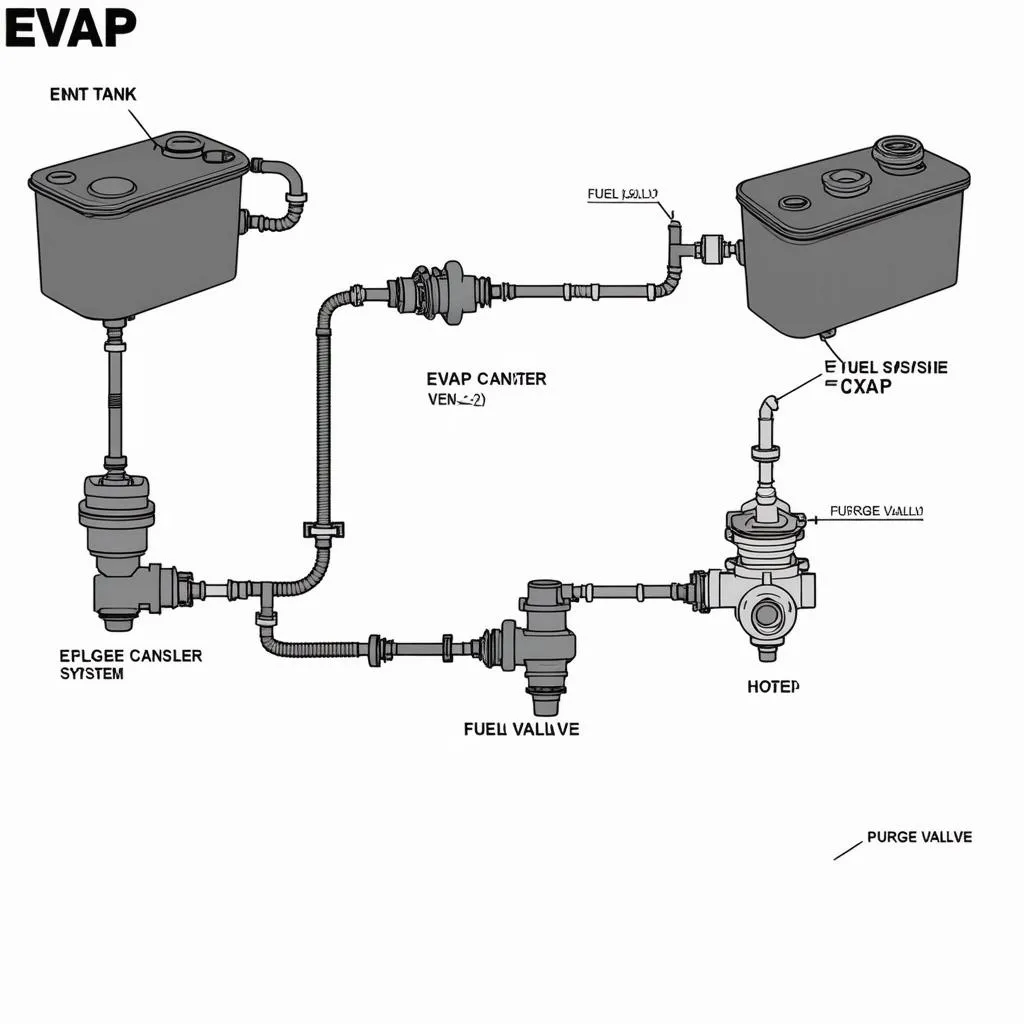 Evaporative Emission System
Evaporative Emission System
 OBD2 Scanner
OBD2 Scanner
 2003 Honda Pilot
2003 Honda Pilot